Cognitive scientist Tomer Ullman, head of Harvard’s Computation, Cognition, and Development lab, may have inadvertently blundered into an untapped vein of LEGO Icon inspiration when his interest in AI led him to stage recreations of famous psych experiments.
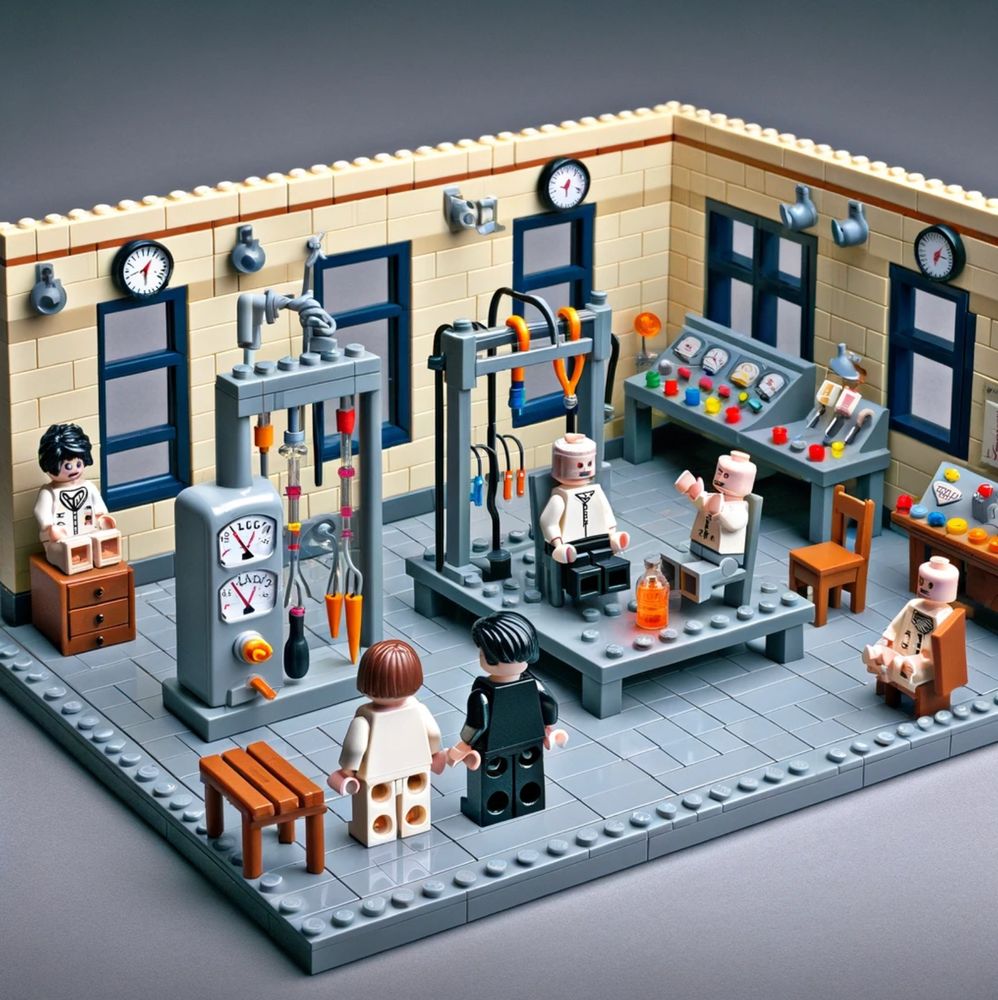
If you think Vincent Van Gogh’s Starry Night LEGO playset is a challenge, imagine putting together the AI-generated playset inspired by Yale psychologist Stanley Milgram’s 1961 obedience studies, above.
Participants in these studies were assigned to play one of two parts — teacher or learner. Partner pairs were seated in separate rooms, accessible to each other by microphones. The teacher read the learner a list of matched words they’d expected to remember shortly thereafter. If the learner flubbed up, the teacher was to administer an electric shock via a series of labelled switches, upping it by 15-volts for each successive error. The microphones ensured that the teacher was privy to the learner’s increasingly distressed reactions — screams, desperate protestation, and — at the highest voltage — radio silence.
Should a teacher hesitate, they’d be reminded that the parameters of the experiment, for which they were earning $4.50, required them to continue. They also received reassurance that the painful shocks caused no permanent tissue damage.
Here’s the thing:
The teachers were innocent as to the experiment’s true nature. They thought the study’s focus was punishment’s effect on learning ability, but in fact, Milgram was studying the limits of obedience to authority.
The learners were all in on the ruse. They received no shocks. Their responses were all feigned.
If our eyes don’t deceive us, the Milgram experiment that the AI imagines is even more extreme than the original. It appears all participants, including those waiting for their turn, are in the same room.
As someone commented on Bluesky, the new social media platform on which Ullman shared his hypothetical playsets, “the subtle details the AI has got wrong here are the stuff of nightmares.”
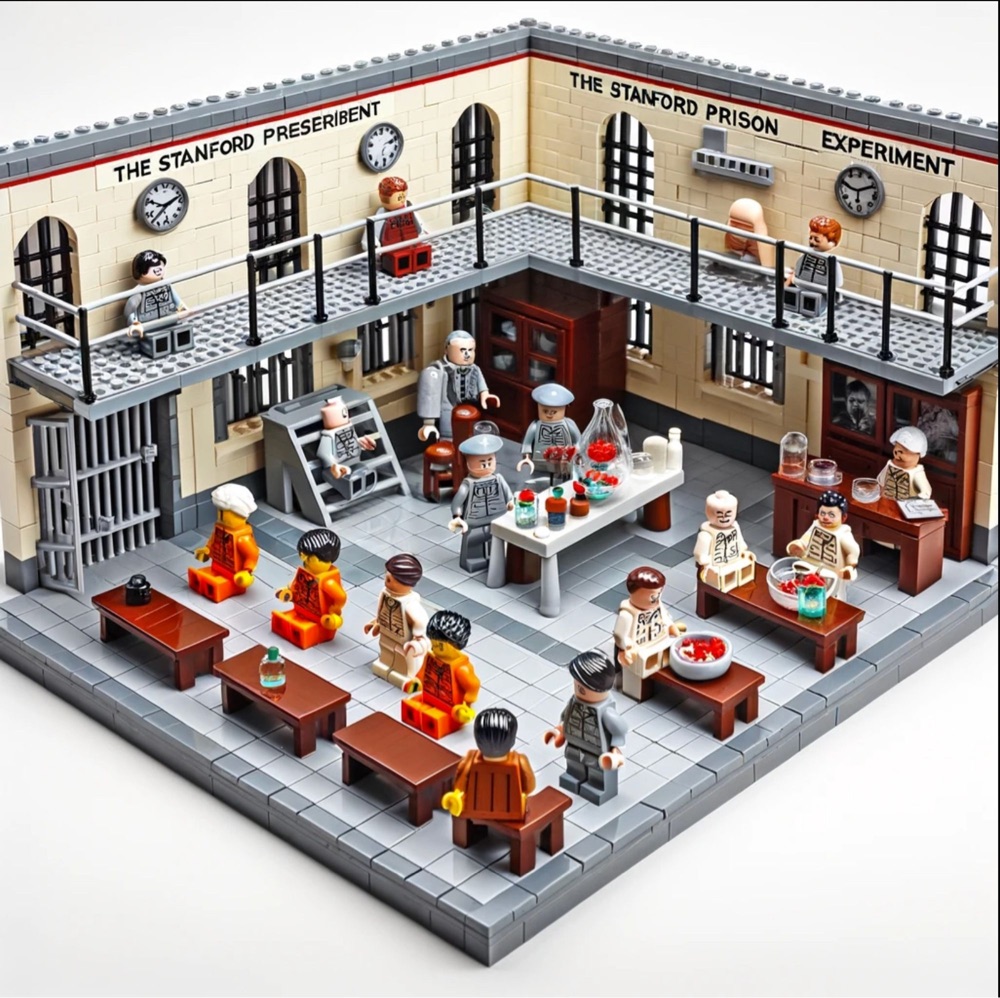

AI’s take on the Stanford prison experiment seems more benign than the controversial 1971 experiment that recruited 24 student participants for a filmed study of prison life to be staged in Stanford University’s psychology department’s basement, randomly dividing them into prisoners and guards.
AI’s faithful recreation of the LEGO figurines’ physical limitations can’t really capture the faux guards’ brutality — making their prisoners clean out toilets with their bare hands, stripping them naked, and depriving them of food and beds. Their power abuses were so wanton, and the prisoners’ distress so extreme, that the planned duration of two weeks was scrapped six days in.
It’s worth noting that all the student participants came to the study with clean bills of physical and mental health, and no histories of criminal arrest.
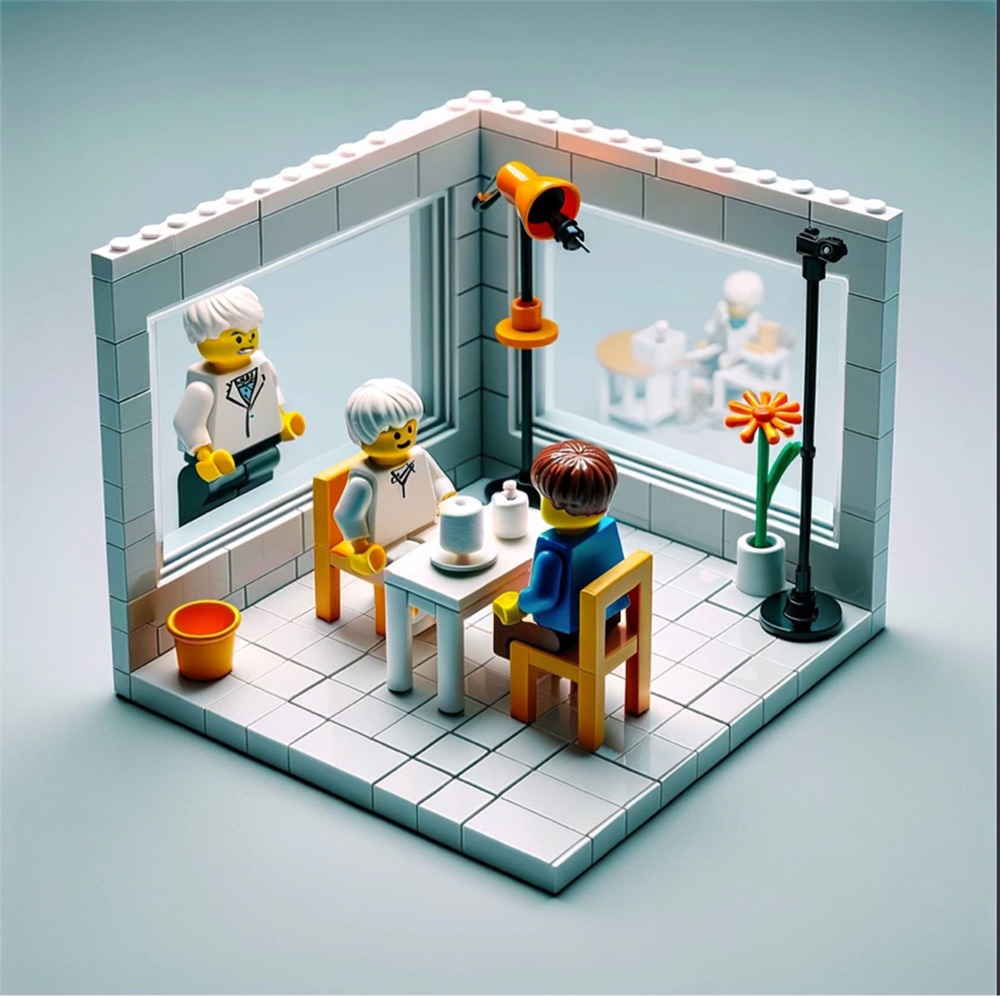
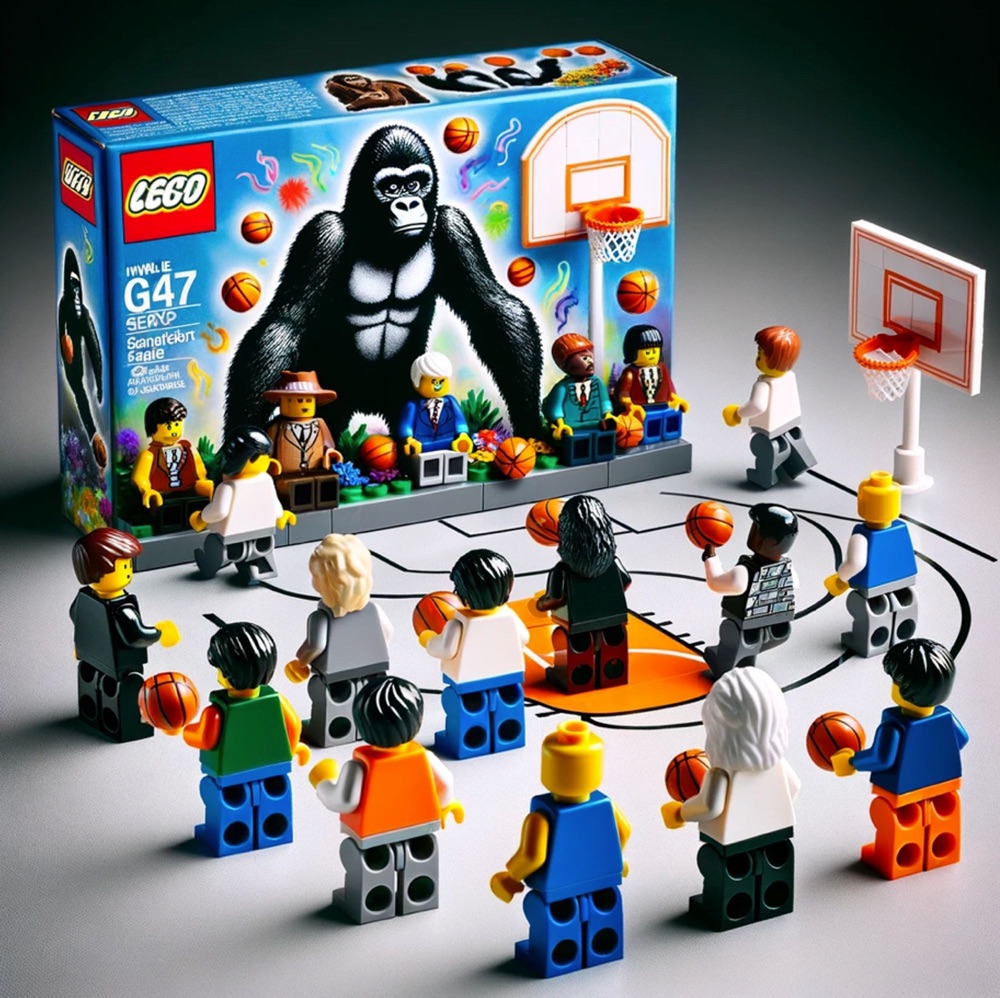


Far less upsetting are the cognitive science experiment playsets depicting the delayed gratification of the Stanford Marshmallow Test and the selective attention of the Invisible Gorilla Test (both right above).
Ullman also steered AI toward LEGO tributes to B.F. Skinner’s operant conditioning chamber and Martin Seligman’s learned helplessness research (below).
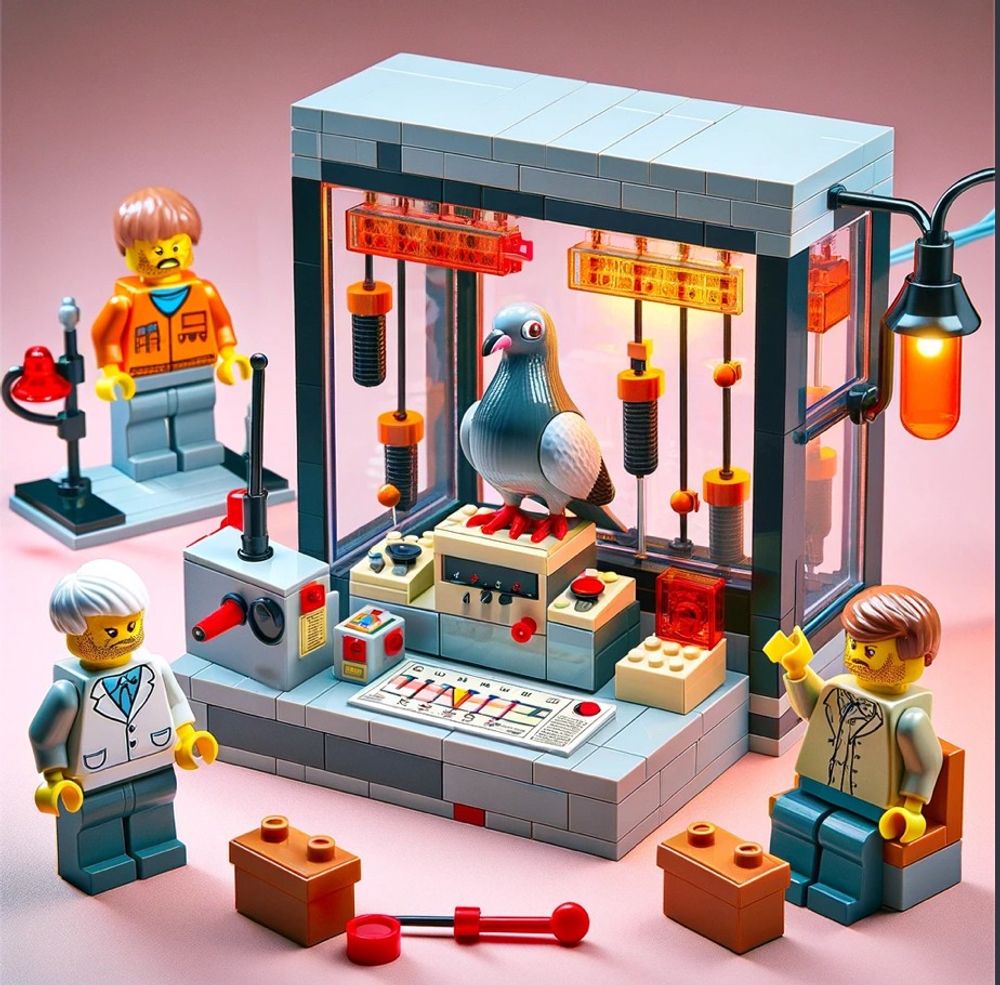


No word on whether he has plans to continue experimenting with AI-engineered LEGO playset proposals featuring historic experiments of psychology and cognitive science.
Follow on Bluesky if you’re curious. You’ll need to register for a free account and apply for an invite code, if you haven’t already… wait, are we setting ourselves up to be unwitting participants in another psych experiment?
Hmmm…
Via Kottke
Related Content
The Psychology Experiment That Shocked the World: Milgram’s Obedience Study (1961)
– Ayun Halliday is the Chief Primatologist of the East Village Inky zine and author, most recently, of Creative, Not Famous: The Small Potato Manifesto and Creative, Not Famous Activity Book. Follow her @AyunHalliday.