|
How Marcel Duchamp Signed a Urinal in 1917 & Redefined Art, Richard Feynman Creates a Simple Method for Telling Science From Pseudoscience (1966) ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
|
| |

|
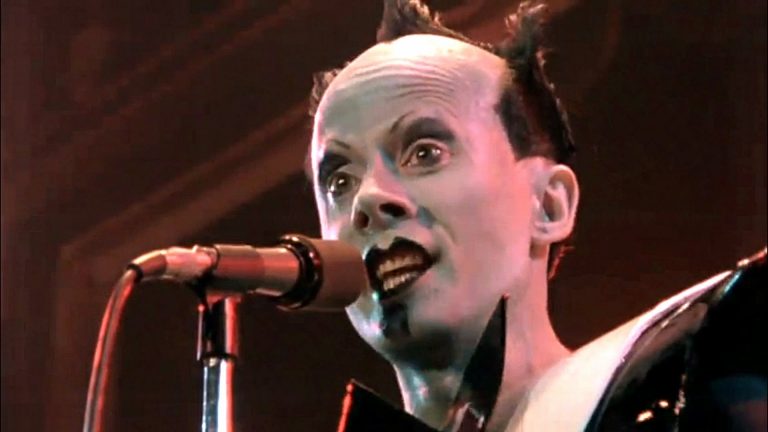
After making one of the grandest entrances in music history on the stages of East Village clubs, the BBC’s The Old Grey Whistle Test, and Saturday Night Live, theatrical German new wave space alien Klaus Nomi died alone in 1983, a victim of the “first beachhead of the AIDS epidemic.” The disease frightened…
|
|
|
|
| |

|
Marcel Duchamp didn’t sign his name on a urinal for lack of ability to create “real” art. In fact, as explained by gallerist-Youtuber James Payne in the new Great Art Explained video above, Duchamp’s grandfather was an artist, as were three of his siblings; he himself attained impressive technical proficiency in painting by…
|
|
|
|
| |

|
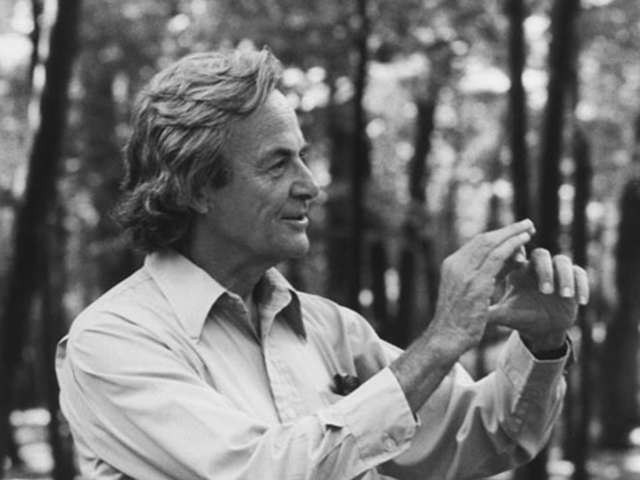
Photo by Tamiko Thiel via Wikimedia Commons
How can we know whether a claim someone makes is scientific or not? The question is of the utmost consequence, as we are surrounded on all sides by claims that sound credible, that use the language of science—and often do so in attempts to refute…
|
|
|
|
| |
|
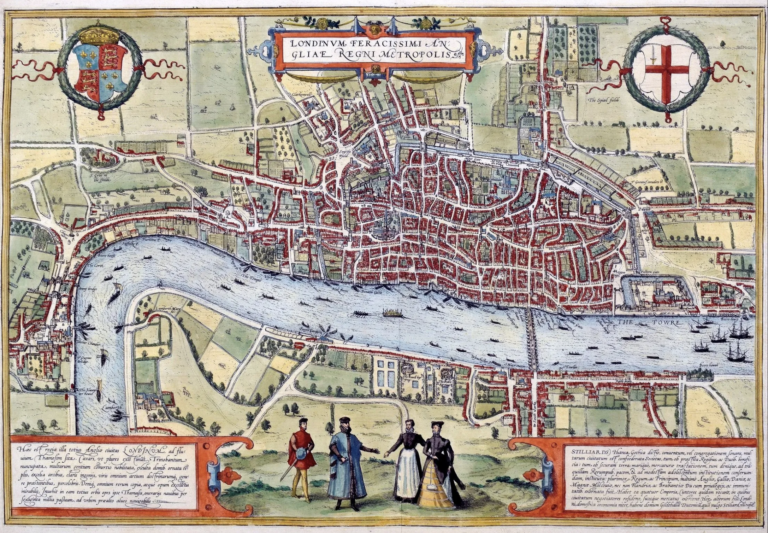
Read a novel by Charles Dickens, and you’ll still today feel transported back to the London of the eighteen-twenties. Some of that experience owes to his lavishly reportorial descriptive skills, but even more to his way with dialogue. Dickens faithfully captured the vocabulary of the times and places in which he set his stories, and…
|
|
|
|