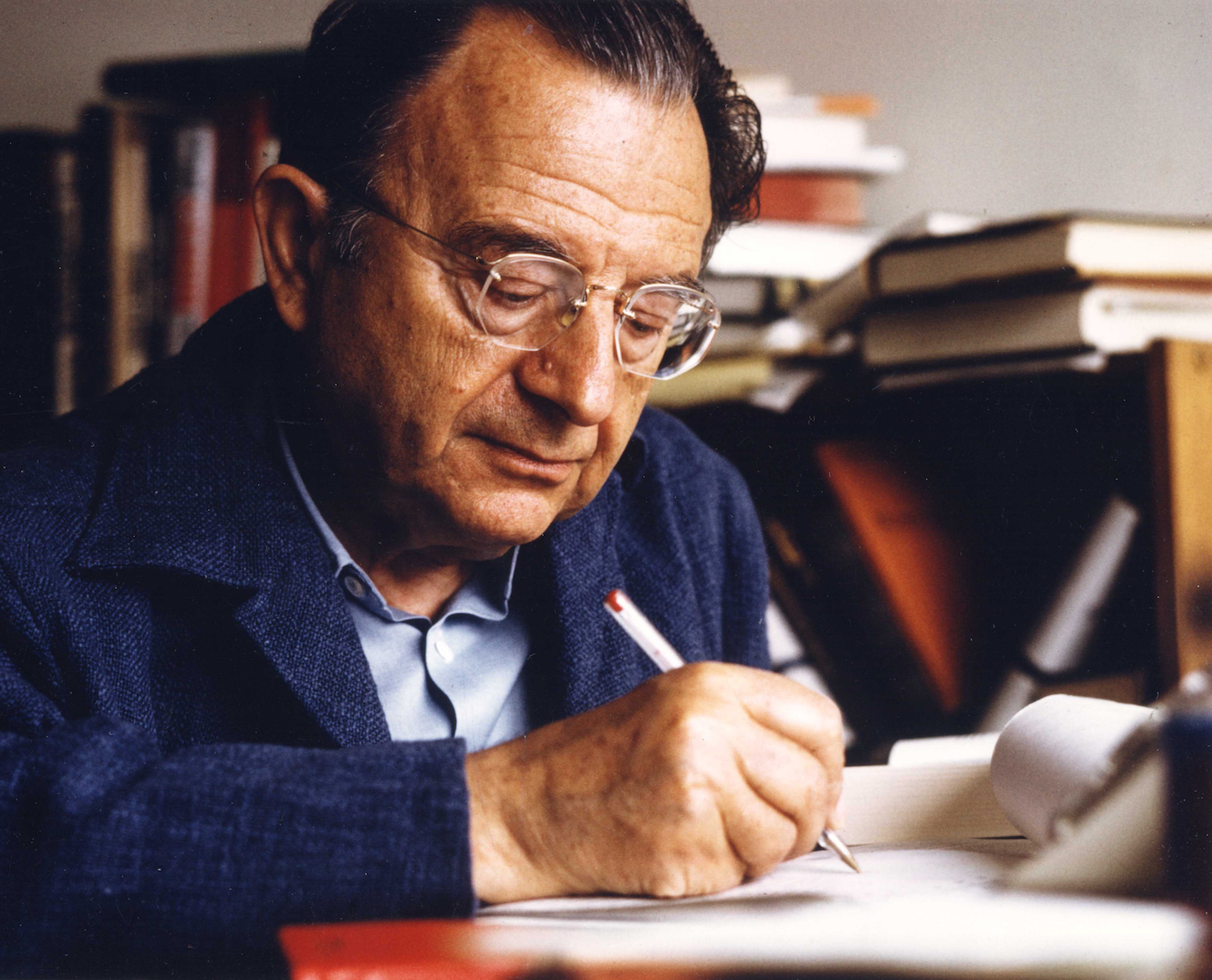
Photo by Müller-May/Rainer Funk, via Wikimedia Commons
The social psychologist and philosopher Erich Fromm lived through just about the first 80 years of the 20th century, beginning in Germany, ending in Switzerland, and spending periods in between in places like New York, Mexico City, and Lansing, Michigan. But his intellectual experience exceeded even his clearly formidable historical and cultural experience: he engaged in not just psychoanalytic theory and practice but theological scholarship, political critique, and what he called a kind of “mysticism.”
To the wider public, which first got to know him through his 1956 bestseller The Art of Loving: An Enquiry into the Nature of Love, Fromm — who had already experienced so much of humanity — was an authority on human relationships. Before one can love, one must, in a broad sense, be able to listen, and he treats that subject at length in The Art of Listening, a posthumously published book adapted from a 1974 seminar in Switzerland.
Speaking in terms of psychoanalysis, Fromm objects to framing listening as a “technique,” since that word applies “to the mechanical, to that which is not alive, while the proper word for dealing with that which is alive is ‘art.’ ” And so if “psychoanalysis is a process of understanding man’s mind, particularly that part which is conscious… it is an art like the understanding of poetry.” He then provides six basic rules for this art as follows:
- The basic rule for practicing this art is the complete concentration of the listener.
- Nothing of importance must be on his mind, he must be optimally free from anxiety as well as from greed.
- He must possess a freely-working imagination which is sufficiently concrete to be expressed in words.
- He must be endowed with a capacity for empathy with another person and strong enough to feel the experience of the other as if it were his own.
-
The condition for such empathy is a crucial facet of the capacity for love. To understand another means to love him — not in the erotic sense but in the sense of reaching out to him and of overcoming the fear of losing oneself.
-
Understanding and loving are inseparable. If they are separate, it is a cerebral process and the door to essential understanding remains closed.
Fromm’s rules apply not just outside his profession but independently of era or culture: wherever you are or whenever it happens to be, you can always practice freeing your mind so as to concentrate as completely as possible on the person talking to you, honing your imagination so as to vividly experience in your mind what they have to verbally communicate. Of course, to love, in Fromm’s sense, remains a particular challenge in this process, and for humans may well stand as the challenge of existence. But whether or not you credit psychoanalysis itself, the fact remains that we all must, to the greatest extent possible, understand one another’s minds as our own; the very survival of humanity has always depended on it.
via Brain Pickings
Related Content:
The Power of Empathy: A Quick Animated Lesson That Can Make You a Better Person
We Are Wired to Be Kind: How Evolution Gave Us Empathy, Compassion & Gratitude
How to Listen to Music: A Free Course from Yale University
Learn 48 Languages Online for Free: Spanish, Chinese, English & More
Based in Seoul, Colin Marshall writes and broadcasts on cities and culture. His projects include the book The Stateless City: a Walk through 21st-Century Los Angeles and the video series The City in Cinema. Follow him on Twitter at @colinmarshall or on Facebook.