
Flash is finally dead, and the world… does not mourn. Because the announcement of its end actually came three years ago, “like a guillotine in a crowded town square,” writes Rhett Jones at Gizmodo. It was a slow execution, but it was just. So useful in Web 1.0 days for making animations, games, and serious presentations, Flash had become a vulnerability, a viral carrier that couldn’t be patched fast enough to keep the hackers out. “Adobe’s Flash died many deaths, but we can truly throw some dirt on its grave and say our final goodbyes because it’s getting the preservation treatment.” Like the animated GIF, Flash animations have their own online library.
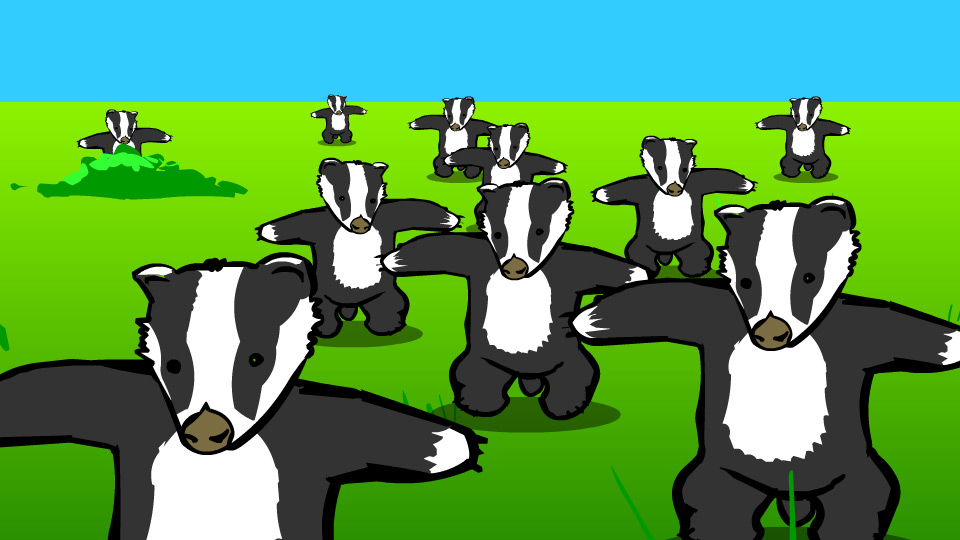

All those lovely Flash memes—the dancing badgers and the snake, peanut butter and jelly time—will be saved for perplexed future generations, who will use them to decipher the runes of early 2000’s internet-speak. However silly they may seem now, there’s no denying that these artifacts were once central constituents of pop culture.
Flash was much more than a distraction or frustrating browser crasher. It provided a “gateway,” Jason Scott writes at the Internet Archive blog, “for many young creators to fashion near-professional-level games and animation, giving them the first steps to a later career.” (Even if it was a career making “advergames.”)
A single person working in their home could hack together a convincing program, upload it to a huge clearinghouse like Newgrounds, and get feedback on their work. Some creators even made entire series of games, each improving on the last, until they became full professional releases on consoles and PCs.
Always true to its purpose, the Internet Archive has devised a way to store and play Flash animations using emulators created by Ruffle and the BlueMaxima Flashpoint Project, who have already archived tens of thousands of Flash games. All those adorable Homestar Runner cartoons? Saved from extinction, which would have been their fate, since “without a Flash player, flash animations don’t work.” This may seem obvious, but it bears some explanation. Where image, sound, and video files can be converted to other formats to make them accessible to modern players, Flash animations can only exist in a world with Flash. They are like Edison’s wax cylinders, without the charming three-dimensions.
Scott goes into more depth on the rise and fall of Flash, a history that begins in 1993 with Flash’s predecessor, SmartSketch, which became FutureWave, which became Flash when it was purchased by Macromedia, then by Adobe. By 2005, it started to become unstable, and couldn’t evolve along with new protocols. HTML5 arrived in 2014 to issue the “final death-blow,” kind of.… Will Flash be missed? It’s doubtful. But “like any container, Flash itself is not as much of a loss as all the art and creativity it held.” The Archive currently hosts over 1,500 Flash animations from those turn-of-the-millennium internet days, and there are many more to come. Enter the Archive’s Flash collection here.
Related Content:
36,000 Flash Games Have Been Archived and Saved Before Flash Goes Extinct: Play Them Offline
What the Entire Internet Looked Like in 1973: An Old Map Gets Found in a Pile of Research Papers
Josh Jones is a writer and musician based in Durham, NC. Follow him at @jdmagness

