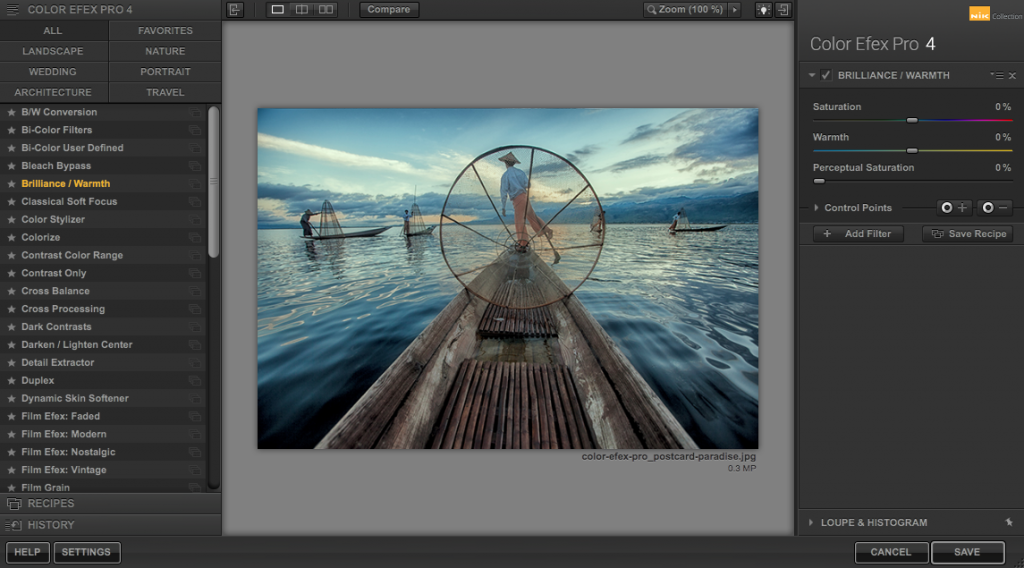
In March of 2016, readers thrilled when Google announced that it made the Nik Collection, its professional photo editing software, free to download and use. Previously priced at $149, the now-free software gives users access to “seven desktop plug-ins that provide a powerful range of photo editing capabilities — from filter applications that improve color correction, to retouching and creative effects.”
If there was cause for celebration, it didn’t last that long. Earlier this year, Google followed up with another announcement–that it planned to discontinue development of the Nik Collection, and essentially let it wither on the vine.
Now here’s the latest chapter in the story. A seemingly good one. The image processing company DxO has acquired the Nik Collection from Google. Jérôme Ménière, DxO’s founder and CEO, declared in a press release, “DxO revolutionized the image processing market many times over the years with its innovative solutions, and we will continue to do so with Nik’s tools, which offer new creative opportunities to millions of photographers.” Apparently the Nik Collection gets to live another day.
If you head over to DxO’s website, you can still download the current Nik Collection for free. You simply need to provide your email address, and they’ll send a download link to your inbox.
Also on the DxO website they’ve announced plans for a future iteration of the Nik Collection, saying “The new ‘Nik Collection 2018 Edition’ will be released mid-2018, please leave your email below to be informed when it’s available.” Whether that 2018 edition will stay free remains to be seen.
Related Content:
Google Makes Its $149 Photo Editing Software Now Completely Free to Download
Download New Storyboarding Software That’s Free & Open Source
NASA Puts Its Software Online & Makes It Free to Download