
The poet Tibullus first described Rome as “The Eternal City” in the first century BC, and that evocative nickname has stuck over the thousands of years since. Or rather, he would have called it “Urbs Aeterna,” which for Italian-speakers would have been “La Città Eterna,” but regardless of which language you prefer it in, it throws down a daunting challenge before any historian of Rome. Each scholar has had to find their own way of approaching such a historically formidable place, and few have built up such a robust visual record as Rodolfo Lanciani, 4000 items from whose collection became available to view online this year, thanks to Stanford Libraries.
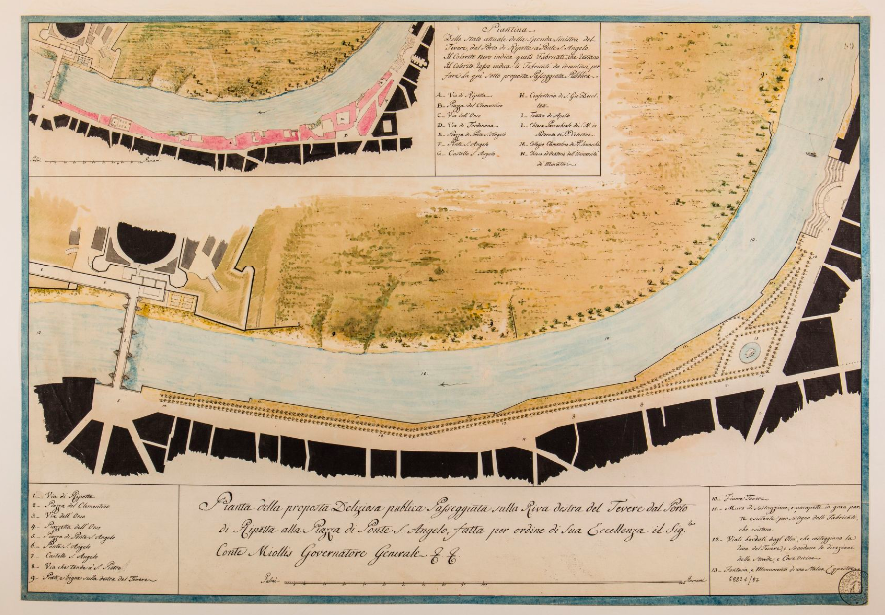
As an “archaeologist, professor of topography, and secretary of the Archaeological Commission,” says the collection’s about page, Lanciani, “was a pioneer in the systematic, modern study of the city of Rome.”
Having lived from 1845 to 1929 with a long and fruitful career to match, he “collected a vast archive of his own notes and manuscripts, as well as works by others including rare prints and original drawings by artists and architects stretching back to the sixteenth century.” After he died, his whole library found a buyer in the Istituto Nazionale di Archeologia e Storia dell’Arte (INASA), which made it available to researchers at the 15th-century Palazzo Venezia in Rome.

Enter a team of professors, archaeologists, and technologists from Stanford and elsewhere, who with a grant from the Samuel H. Kress Foundation, and in partnership with Italy’s Ministry of Cultural Heritage and Activities and Tourism and the National Institute, began digitizing it all. Their efforts have so far yielded an exhibition of about 4,000 of Lanciani’s drawings, prints, photographs and sketches of Rome from the 16th century to the 20th. Not only can you examine them in high-resolution in your browser as well as download them, you can also see the locations of what they depict pinpointed on the map of Rome. That feature might come in especially handy when next you pay a visit to The Eternal City, though for many of the features depicted in Lanciani’s collection, you hardly need directions. Enter the digital collection here.
via Stanford News
Related Content:
The History of Rome in 179 Podcasts
Ancient Rome’s System of Roads Visualized in the Style of Modern Subway Maps
Based in Seoul, Colin Marshall writes and broadcasts on cities and culture. His projects include the book The Stateless City: a Walk through 21st-Century Los Angeles and the video series The City in Cinema. Follow him on Twitter at @colinmarshall or on Facebook.


Leave a Reply