Almost all the biggest math enthusiasts I’ve known have also loved classical music, especially the work of Bach, Mozart, and Beethoven. Of course, as San Francisco Symphony music director Michael Tilson Thomas once put it, you can’t have those three as your favorite composers, because “they simply define what music is.” But don’t tell that to the mathematically minded, on whom all of them, especially Bach and Beethoven, have always exerted a strong pull.
But why? Do their musical compositions have some underlying quantitative appeal? And by the way, “how is it that Beethoven, who is celebrated as one of the most significant composers of all time, wrote many of his most beloved songs while going deaf?” The question comes from a TED-Ed segment and its accompanying blog post by Natalya St. Clair which explains, using the example of the “Moonlight Sonata,” what the formidable composer did it using math. (You might also want to see St. Clair’s other vides: The Unexpected Math Behind Van Gogh’s “Starry Night.”)
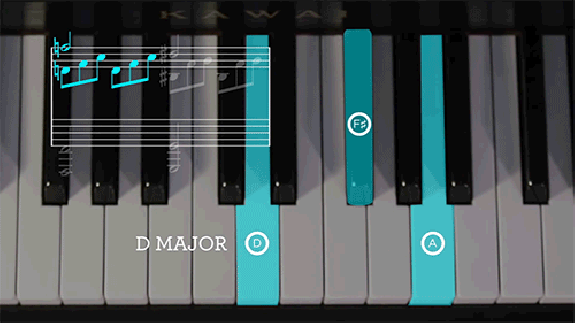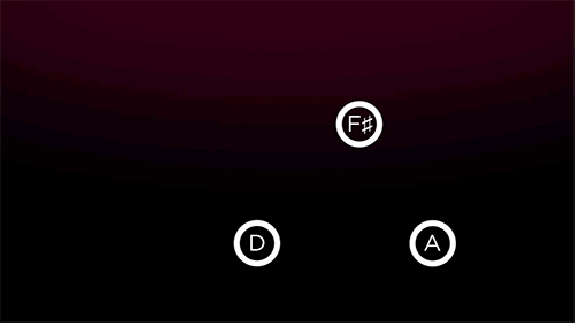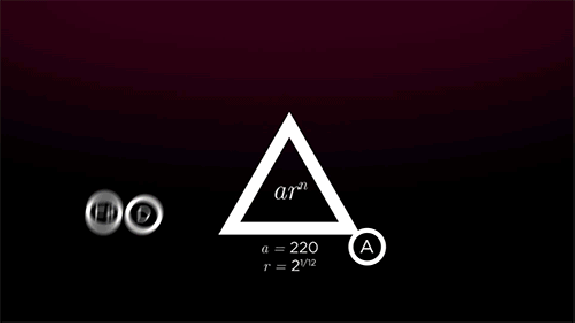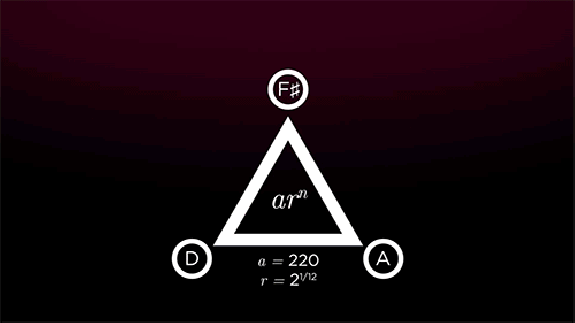
“The standard piano octave consists of 13 keys, each separated by a half step,” St. Clair writes. “A standard major or minor scale uses 8 of these keys with 5 whole step intervals and 2 half step ones.” So far, so good. “The first half of measure 50 of ‘Moonlight Sonata’ consists of three notes in D major, separated by intervals called thirds that skip over the next note in the scale. By stacking the first, third, and fifth notes — D, F sharp, and A — we get a harmonic pattern known as a triad.” These three frequencies together create “ ‘consonance,’ which sounds naturally pleasant to our ears. Examining Beethoven’s use of both consonance and dissonance can help us begin to understand how he added the unquantifiable elements of emotion and creativity to the certainty of mathematics.”
Explained in words, Beethoven’s use of mathematics in his music may or may not seem easy to understand. But it all gets clearer and much more vivid when you watch the TED-Ed video about it, which brings together visuals of the piano keyboard, the musical score, and even the relevant geometric diagrams and sine waves. Nor does it miss the opportunity to use music itself, breaking it down into its constituent sounds and building it back up again into the “Moonlight Sonata” we know and love — and can now, having learned a little more about what mathematician James Sylvester called the “music of the reason” underlying the “mathematics of the sense,” appreciate a little more deeply.
Related Content:
Stream the Complete Works of Bach & Beethoven: 250 Free Hours of Music
Beethoven’s 5th: The Animated Score
Leonard Bernstein Conducts Beethoven’s 9th in a Classic 1979 Performance
Beethoven’s Ode to Joy Played With 167 Theremins Placed Inside Matryoshka Dolls in Japan
Man Hauls a Piano Up a Mountain in Thailand and Plays Beethoven for Injured Elephants
Slavoj Žižek Examines the Perverse Ideology of Beethoven’s Ode to Joy
Oliver Sacks’ Last Tweet Shows Beethoven’s “Ode to Joy” Movingly Flashmobbed in Spain
Based in Seoul, Colin Marshall writes and broadcasts on cities, language, and style. He’s at work on a book about Los Angeles, A Los Angeles Primer, the video series The City in Cinema, the crowdfunded journalism project Where Is the City of the Future?, and the Los Angeles Review of Books’ Korea Blog. Follow him on Twitter at @colinmarshall or on Facebook.