Since the Harry Potter craze began, we’ve seen young adult fiction gain massive popularity with adults, in ways some critics have lamented as a trend that infantilizes the buying public. (Some say the same about superhero films and adult fans of boy bands). Katie Couric identified the phenomenon as “the rise of so-called Peter Pan activities,” throwing “adult summer camps and Lego leagues” in the mix. Critics of Peter Panism can add another trend to their battery of examples: the rise of the adult coloring book. Business Insider reported in April that “in Britain, four out of the top 10 Amazon bestsellers are coloring (or colouring, as the Brits insist) books for adults.” Currently, Amazon’s top 20 bestsellers for 2015 includes three adult coloring books. Among so many other consumer signs and portents, adult coloring books may indeed herald a coming apocalypse, at least for Russell Brand, who wonders, “What has turned us into terrified divs that want to live in childish stupors?”
Well, whether “childish,” art therapy or “Zen,” adult coloring books meet a need millions of grown-ups have to soothe their jangled nerves, and it seems almost cruel to mock people so anxiety-ridden they’ve returned to kindergarten remedies. Then again, it’s worth noting, as Smithsonian did recently, “the adult coloring concept is not exactly new.”
It dates back to the 1960s, when “bookstores exploded” with coloring books geared exclusively toward adults. The difference between then and now lies in the fact that those books were adult in content as well as form—“satirical and subversive,” offering “a mocking look at American society.” The first of these, The Executive Coloring Book, arrived in 1961, followed by The John Birch Society Coloring Book and many similar titles “satirizing conformism, John F. Kennedy and the Soviet Union,” among other targets. And yet, “Unlike the adult coloring books flying off the shelves today,” Smithsonian writes, “these books were not created with the intention to be colored in.”
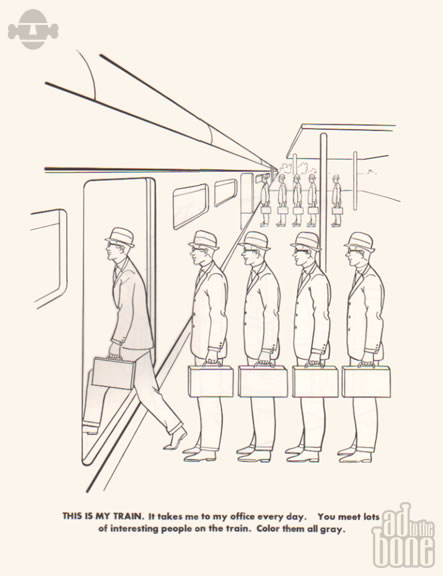
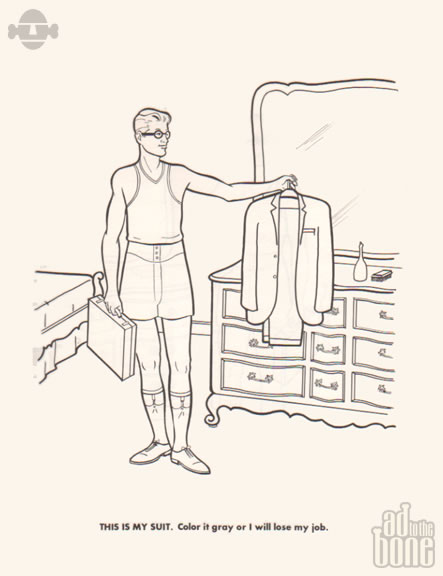
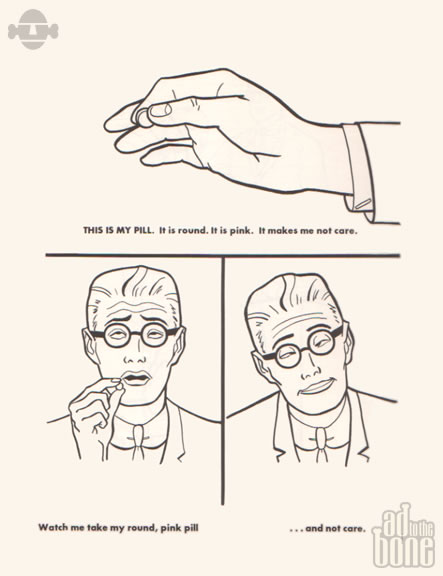
Take the two pages from The Executive Coloring Book above. The first, at the top, shows us our executive preparing for his day with the caption “THIS IS MY SUIT. Color it gray or I will lose my job.” Above, a line of identical executives boards a train. Hammering home the point, we’re told “THIS IS MY TRAIN. It takes me to my office every day. You meet lots of interesting people on the train. Color them all gray.” A notable exception to these dreary instructions, below, tells us “THIS IS MY PILL. It is round. It is pink. It makes me not care. Watch me take my round, pink pill… and not care.” The contents of the pill may have changed, but the medicated worker bee is still very much with us, though the gray flannel suit is a thing of the past.
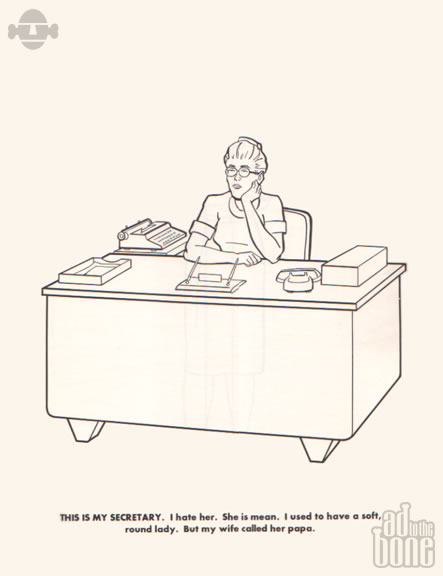
Rather than giving its target audience a chance to become kids again, The Executive Coloring Book pokes fun at the ways in which pampered executives of the Mad Men-era could themselves be shallow manchildren. One page, below, shows the executive’s secretary with the caption “THIS IS MY SECRETARY. I hate her. She is mean. I used to have a soft, round lady. But my wife called her papa.” Another (bottom), reminiscent of the business card scene in American Psycho, shows us the executive’s important phone: “THIS IS MY TELEPHONE. It has five buttons. Count them. One, two, three, four, five. Five buttons. How many buttons does your telephone have? Mine has five.”

From its faux-leather cover to its final page of business-speak gibberish, the whole thing is a masterfully simple, self-contained piece of conceptual art. The next publication by the same authors, The John Birch Coloring Book, made its intentions a little more obvious. A Sunday Herald review quotes from its introduction: “This book is respectfully dedicated to Dwight D. Eisenhower and many other loyal Americans who have been maligned by extremist groups.” One caption reads “This is our eagle. We cut off his left wing. Now he is an all American eagle. But he flies only in circles.” The “Birchers will have to learn to smile,” writes the reviewer, as the book “spare[s] not their feelings.” Not likely. Rather than selling relaxation, the adult coloring books of the 60s were “engaged,” wrote Milton Bracker in a 1962 New York Times review, “in political warfare.”

via Smithsonian and Ad to the Bone
Related Content:
Download 15,000+ Free Golden Age Comics from the Digital Comic Museum
Dr. Seuss Draws Anti-Japanese Cartoons During WWII, Then Atones with Horton Hears a Who!






