Do you want to speak more languages? Sure, as Sally Struthers used to say so often, we all do. But the requirements of attaining proficiency in any foreign tongue, no doubt unlike those correspondence courses pitched by that All in the Family star turned daytime TV icon, can seem frustratingly demanding and unclear. But thanks to the research efforts of the Foreign Service Institute, the center of foreign-language training for the United States government for the past 70 years, you can get a sense of how much time it takes, as a native or native-level English speaker, to master any of a host of languages spoken all across the world.
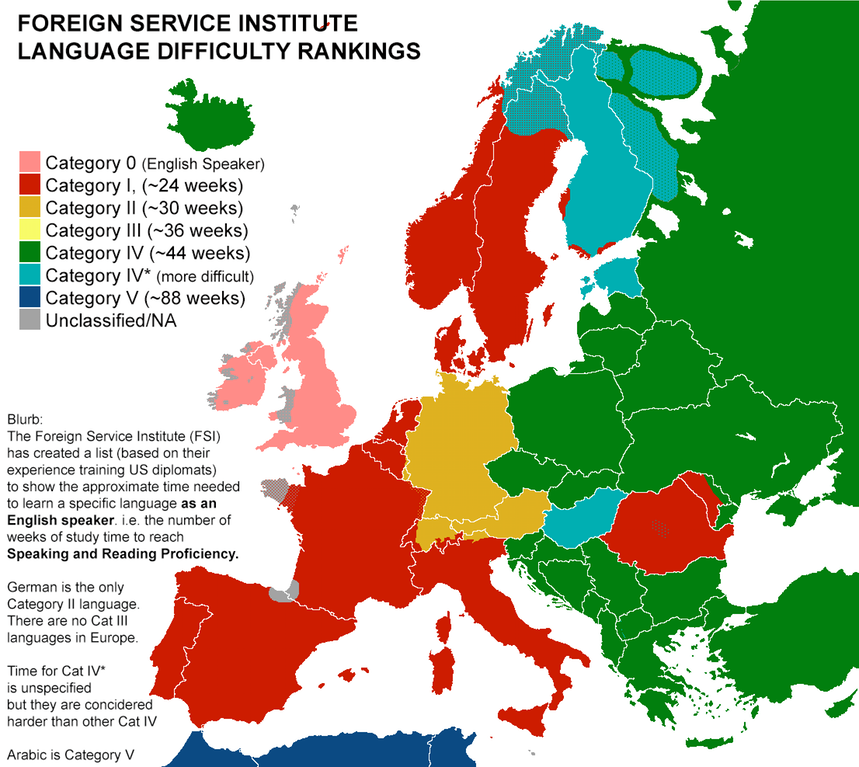
The map above visualizes the languages of Europe (at least those deemed diplomatically important enough to be taught at the FSI), coloring them according the average time commitment they require of an English speaker. In pink, we have the English-speaking countries. The red countries speak Category I languages, those most closely related to English and thus learnable in 575 to 600 hours of study: the traditional high-school foreign languages of Spanish and French, for instance, or the less commonly taught but just about as easily learnable Portuguese and Italian. If you’d like a little more challenge, why not try your hand at German, whose 750 hours of study puts it in Category II — quite literally, a category of its own?
In total, the FSI ranks languages into six categories of difficulty, including English’s Category 0. The higher up the scale you go, the less recognizable the languages might look to an English-speaking monoglot. Category III contains no European languages at all (though it does contain Indonesian, widely regarded as one of the objectively easiest languages to learn). Category IV offers a huge variety of languages from Amharic to Czech to Nepali to Tagalog, each demanding 44 weeks (or 1100 hours) of study. Then, at the very summit of the linguistic mountain, we find the switched-up grammar, highly unfamiliar scripts, and potentially mystifying cultural assumptions of Category V, “languages which are exceptionally difficult for native English speakers.”
To that most formidable group belong Arabic, Chinese both Mandarin and Cantonese, Korean, and — this with an asterisk meaning “usually more difficult than other languages in the same category” — Japanese. Now if, like me, you consider studying foreign languages one of your main pursuits, you know that possessing a genuine interest in a language — in its mechanics, in its ongoing evolution, in the cultures that created it and the cultures it in turn creates — can do wonders to get you through even the most aggravating difficulties on the long journey to commanding it. Then again, I’m also a native English speaker who chose to move to Korea, where I study not just the Category‑V Korean but the Category‑V* Japanese through Korean; you might want to take with a grain of salt the words, in any language, of so obvious a masochist.
You’ll find the full Foreign Service Institute language difficulty ranking list below. No matter which category you’d like to take on, you can get a start at our Free Foreign Language Lessons collection, many of whose materials come produced by the FSI itself.
Category I: 23–24 weeks (575–600 hours)Languages closely related to EnglishAfrikaansDanishDutchFrenchItalianNorwegianPortugueseRomanianSpanishSwedishCategory II: 30 weeks (750 hours)Languages similar to EnglishGermanCategory III: 36 weeks (900 hours)Languages with linguistic and/or cultural differences from EnglishIndonesianMalaysianSwahiliCategory IV: 44 weeks (1100 hours)Languages with significant linguistic and/or cultural differences from EnglishAlbanianAmharicArmenianAzerbaijaniBengaliBosnianBulgarianBurmeseCroatianCzech*Estonian*Finnish*GeorgianGreekHebrewHindi*HungarianIcelandicKhmerLaoLatvianLithuanianMacedonian*MongolianNepaliPashtoPersian (Dari, Farsi, Tajik)PolishRussianSerbianSinhalaSlovakSlovenianTagalog*ThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbek*VietnameseXhosaZuluCategory V: 88 weeks (2200 hours)Languages which are exceptionally difficult for native English speakersArabicCantonese (Chinese)Mandarin (Chinese)*JapaneseKorean* Usually more difficult than other languages in the same category.
Related Content:
Learn 48 Languages Online for Free: Spanish, Chinese, English & More
The Tree of Languages Illustrated in a Big, Beautiful Infographic
Where Did the English Language Come From?: An Animated Introduction
Based in Seoul, Colin Marshall writes and broadcasts on cities and culture. His projects include the book The Stateless City: a Walk through 21st-Century Los Angeles and the video series The City in Cinema. Follow him on Twitter at @colinmarshall or on Facebook.





