I freely admit it—like a great many people these days, I have a social media addiction. My drug of choice, Twitter, can seem like a particularly schizoid means of acquiring and sharing information (or knee-jerk opinion, rumor, innuendo, nonsense, etc.) and a particularly accelerated form of distractibility that never, ever sleeps. Given the profound degree of over-stimulation such outlets provide, we might be justified in thinking we owe our short attention spans to 21st century technological advances. Not necessarily, says Michigan State University professor Natalie Phillips—who studies 18th and 19th century English literature from the perspective of a 21st century cognitive theorist, and who cautions against “adopting a kind of historical nostalgia, or assuming those of the 18th century were less distracted than we are today.”
Early modern writers were just as aware of—and as concerned about—the problem of inattention as contemporary critics, Phillips argues, “amidst the print-overload of 18th-century England.” We might refer, for example, to Alexander Pope’s epic satire “The Dunciad,” a hilariously apocalyptic jeremiad against the proliferation of careless reading and writing in the new media environment of his day. (A world “drowning in print, where everything was ephemeral, of the moment.”)
Phillips focuses on the work of Jane Austen, whom, she believes, “was drawing on the contemporary theories of cognition in her time” to construct distractible characters like Pride and Prejudice’s Elizabeth Bennett. Taking her cues from Austen and other Enlightenment-era writers, as well as her own inattentive nature, Phillips uses contemporary neuroscience to inform her research, including the use of brain imaging technology and computer programs that track eye movements.
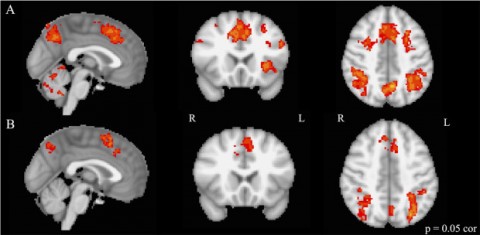
In collaboration with Stanford’s Center for Cognitive and Biological Imaging (CNI), Phillips devised an experiment in 2012 in which she asked literary PhD candidates—chosen, writes Stanford News, “because Phillips felt they could easily alternate between close reading and pleasure reading”—to read a full chapter from Austen’s Mansfield Park, projected onto a mirror inside an MRI scanner. At times, the subjects were instructed to read the text casually, at others, to read closely and analytically. Afterwards, they were asked to write an essay on the passages they read with attention. As you’ll hear Phillips describe in the short NPR piece above, the neuroscientists she worked with told her to expect only the subtlest of differences between the two types of reading. The data showed otherwise. Phillips describes her surprise at seeing “how much the whole brain, global activations across a number of different regions, seems to be transforming and shifting between the pleasure and the close reading.” As CNI neuroscientist Bob Dougherty describes it, “a simple request to the participants to change their literary attention can have such a big impact on the pattern of activity during reading,” with close reading stimulating many more areas of the brain than the casual variety. What are we to make of these still inconclusive results? As with many such projects in the emerging interdisciplinary field of “literary neuroscience,” Phillips’ goal is in part to demonstrate the continued relevance of the humanities in the age of STEM. Thus, she theorizes, the practice and teaching of close reading “could serve—quite literally—as a kind of cognitive training, teaching us to modulate our concentration and use new brain regions as we move flexibly between modes of focus.”
The study also provides us with a fascinating picture—quite literally—of the ways in which the imaginative experience of reading takes place in our bodies as well as our minds. Close, sustained, and attentive reading, Phillips found, activates parts of the brain responsible for movement and touch, “as though,” writes NPR, “readers were physically placing themselves within the story as they analyzed it.” Phillips’ study offers a scientific look at a mysterious experience serious readers know well—“how the right patterns of ink on a page,” says Dougherty, “can create vivid mental imagery and instill powerful emotions.” As with the so-called “hard problem of consciousness,” we may not understand exactly how this happens anytime soon, but we can observe that the experience of close reading is a rewarding one for our entire brain, not just the parts that love Jane Austen. While not everyone needs convincing that “literary study provides a truly valuable exercise of people’s brains,” Phillips’ research may prove exactly that.
Related Content:
Jane Austen, Game Theorist: UCLA Poli Sci Prof Finds Shrewd Strategy in “Cluelessness”
This is Your Brain on Jazz Improvisation: The Neuroscience of Creativity
What Happens When Your Brain is on Alfred Hitchcock: The Neuroscience of Film
Josh Jones is a writer and musician based in Durham, NC. Follow him at @jdmagness