Images courtesy of Sothebys
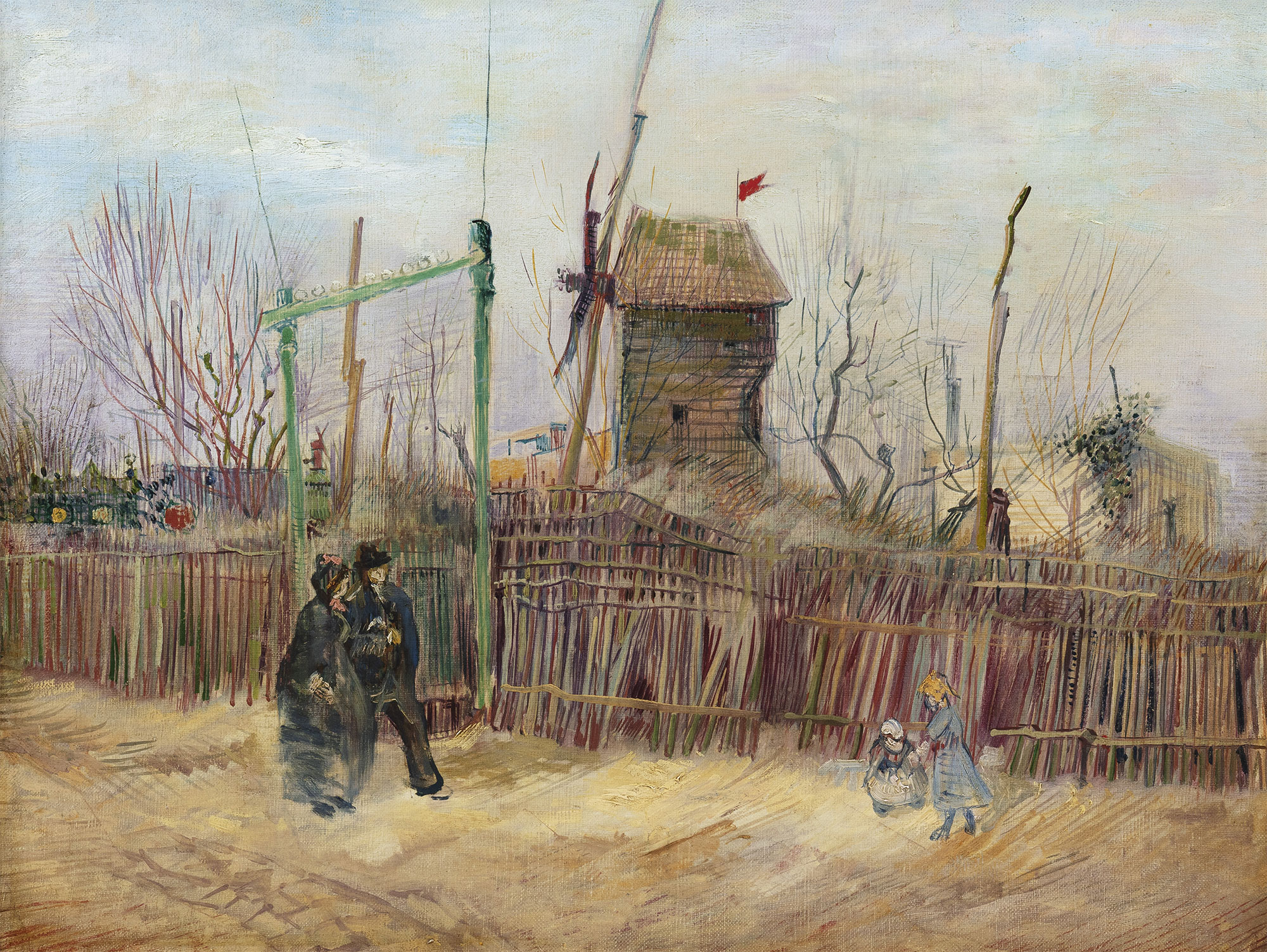
Not every Vincent van Gogh painting hangs at the Van Gogh Museum, or indeed in a museum at all. Though many private collectors loan their Van Goghs to art institutions that make them available for public viewing, some have never let such prized possessions out of their sight. Such, until recently, was the case with Scène de rue à Montmartre (Impasse des Deux Frères et le Moulin à Poivre), painted in 1887 but not shown to the world until this year — in preparation for its auction on March 25. During its century of possession by a single French family, the painting counted as one of the few privately-held entries in Van Gogh’s Montmartre series, which he painted in the eponymous neighborhood during the two years spent in Paris with his brother Theo.
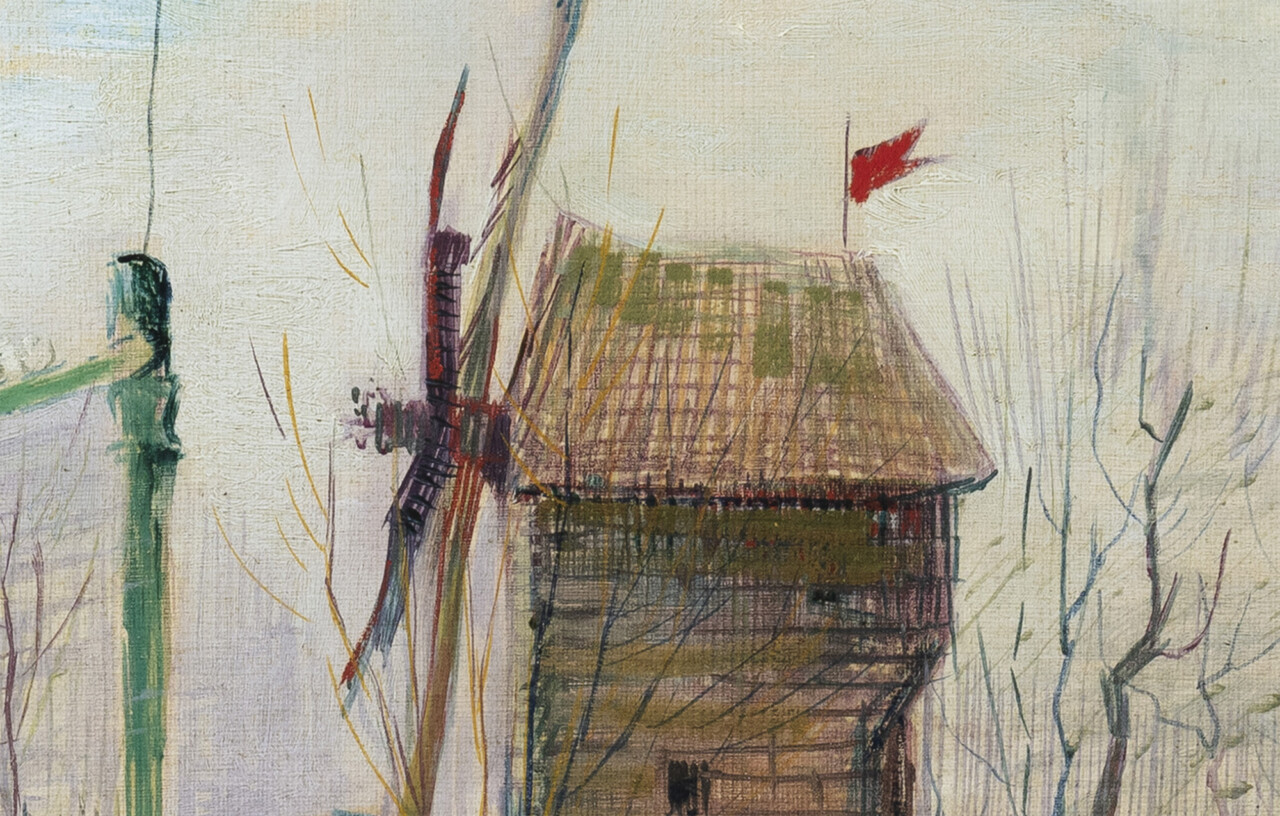

“Unlike other artists of his era, like Toulouse-Lautrec, Van Gogh was attracted to the pastoral side of Montmartre and would transcribe this ambience rather than its balls and cabarets.” So says Aurélie Vandevoorde, head of the Impressionist and Modern Art department at Sotheby’s Paris to The Art Newspaper’s Anna Sanson.
The landscape “marks van Gogh’s turn to his distinctive Impressionist style,” writes Colossal’s Grace Ebert, and its “lively street is thought to be the same as that in Impasse des Deux Frères, which currently hangs at the Van Gogh Museum in Amsterdam, and similarly depicts a mill and flags promoting the cabaret and bar through the gates.”
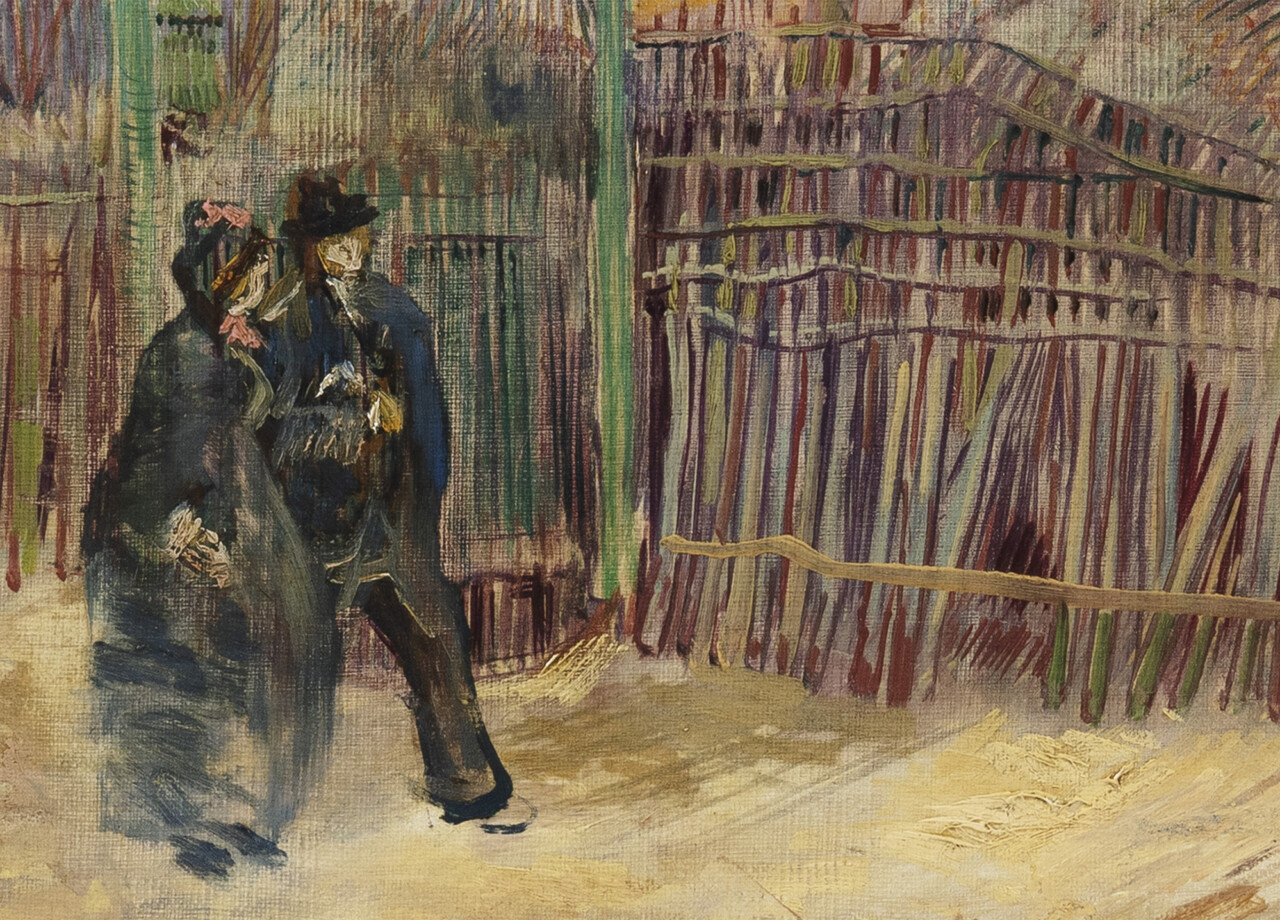

As depicted by Van Gogh more than 130 years ago, Montmartre looks nearly rural — quite unlike it does now, as anyone who’s frequented the neighborhood in living memory can attest. But the status of the painting has changed even more than the status of the place: Scène de rue à Montmartre “is expected to sell for between $6 million and $9.7 million (€5 million to €8 million),” writes Smithsonian.com’s Isis Davis-Marks. Still, like most of Van Gogh’s Paris paintings, its value doesn’t touch that of the work he did in his subsequent Provençal sojourn (under the influence of Japanese ukiyo‑e). “One such painting, Laboureur dans un champ (1889),” adds Davis-Marks, “sold at Christie’s in 2017 for $81.3 million.” Well-heeled readers should thus keep an eye on Sotheby’s site: this could be your chance to keep a (relatively) affordable Van Gogh in your own family for the next century.
via Colossal
Related Content:
Van Gogh’s Ugliest Masterpiece: A Break Down of His Late, Great Painting, The Night Café (1888)
13 Van Gogh’s Paintings Painstakingly Brought to Life with 3D Animation & Visual Mapping
Experience the Van Gogh Museum in 4K Resolution: A Video Tour in Seven Parts
In a Brilliant Light: Van Gogh in Arles – A Free Documentary
Based in Seoul, Colin Marshall writes and broadcasts on cities, language, and culture. His projects include the Substack newsletter Books on Cities, the book The Stateless City: a Walk through 21st-Century Los Angeles and the video series The City in Cinema. Follow him on Twitter at @colinmarshall or on Facebook.