My costume design professor at Northwestern University, Virgil Johnson, delighted students with his formula for period clothing. I have forgotten some of the mathematic and semantic particulars—does dressing someone five years behind the times a “frumpy” character make? Or is it merely one?
I do recall some anxious hours, preparing for the school’s main stage production of the incestuous Jacobean revenge tragedy, ’Tis Pity She’s a Whore. The societal corruption of the play was underscored by having the supporting characters slouch around, snorting mimed cocaine in cutting edge, mid-80s Vogue Patterns … those big unstructured jackets were very a la mode, but they gobbled up a lot of high-budget fabric, and I didn’t want to be the one to make a costly sewing mistake.

What sticks in my mind most clearly is that 20 years was the sweet spot, the appropriate amount of elapsed time to ensure that one would not appear dumpy, dowdy, or oblivious, but rather prudent and discerning. Donning a garment that was 15 years out of fashion might be daringly “retro,” but another five and that same garment could be heralded as “vintage.”
The collaborative Vintage Pattern Wiki puts the magic number at 25, requesting that contributors make sure the patterns they post are from 1992 or earlier, and also out-of-print.
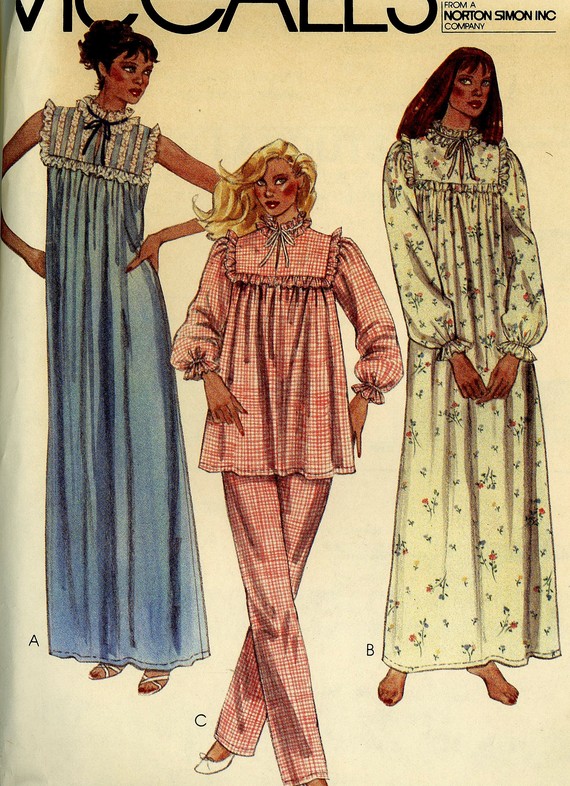

The browsable collection of over 83,500 patterns runs the gamut from Dynasty-inspired pussy bow power suits to Betty Draper-esque frocks featuring models in white gloves to an 1895 boys’ Reefer Suit with fly-free short trousers.
Visitors can narrow their search to focus on a particular garment, designer or decade. If you click these links, you can see patterns from the following decades: 1920s, 1930s, 1940s, 1950s, 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s.
The movie star collection is particularly fun. (Flattering or no, I’ve always wanted a pair of Katharine Hepburn pants…)

And it goes without saying that the dog days of summer are the perfect time to get a jump on your Halloween costume.
Those who are itching to get sewing should check the links below each pattern envelope cover for vendors who have the pattern in stock and photos and posts by community members who have made that same garment.
The prices and handwritten jottings of the original owners will also put you in a vintage mood.
The hunt starts here.

Related Content:
The Online Knitting Reference Library: Download 300 Knitting Books Published From 1849 to 2012
Frida Kahlo’s Colorful Clothes Revealed for the First Time & Photographed by Ishiuchi Miyako
Ayun Halliday is an author, illustrator, theater maker and Chief Primatologist of the East Village Inky zine. Follow her @AyunHalliday.