Cartoonist turned educator Lynda Barry is again permitting the world at large to freely audit one of her fascinating University of Wisconsin-Madison classes via her Tumblr. (To get to the start of the class, click here and then scroll down the page until you reach the syllabus, then start working your way backwards.)
The topic this fall is “Graphic Vices, Graphic Virtues: Making Comics,” a subject with which Barry is intimately acquainted. In the professor’s own words, this class is “a(n academically rigorous) blast!”
As in previous classes, the syllabus, above, spells out a highly specialized set of required supplies, including a number of items rarely called for at the college level.

It’s become a time honored tradition for Barry’s students to adopt new names by which to refer to each other in-class, something they’ll enjoy hearing spoken aloud. For “Making Comics,” Barry is flying under the handle Professor SETI (as in “search for extraterrestrial intelligence”), telling the class that “images are the ETI in SETI.”
The students have responded with the following handles: Chef Boyardee, Ginger, Lois Lane, Rosie the Riveter, Regina Phalange, Arabella, Snoopy, Skeeter, Tigger, Arya Stark, Nala, Nostalgia, Akira, Lapus Lazuli, The Buffalo,Mr. November, The Short Giraffe, Nicki Minaj, Neko, Vincent Brooks, Regular Sized Rudy, and Zef.
(Sounds like a rough and ready crew. What name would you choose, and why?)
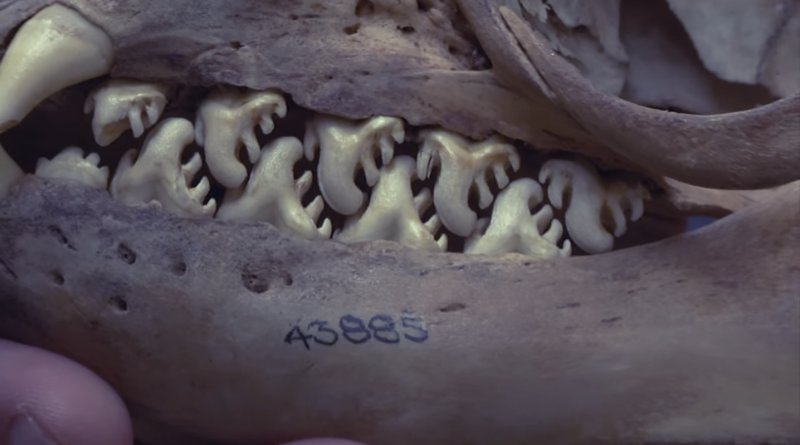
As usual, Barry draws inspiration from the dizzying bounty of images available on the net, bombarding her pupils with findings such as the lobed teeth of the crab-eater seal, above.
Science and music remain pet subjects–Afrofuturist bandleader Sun Ra serves as class oracle this go round.


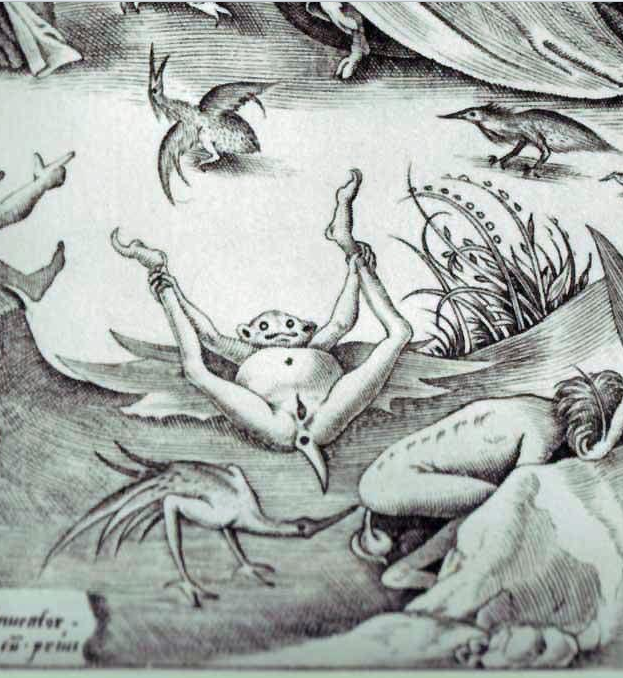
Professor SETI keeps the “graphic vice” of the class’ official title front and center with assignments pertaining to the 7 deadly sins, asking students to examine modern equivalents of the horrors depicted by Heronimus Bosch above and 16th-century engraver Pieter van der Heyden, below.

What to do with all of these images? Draw them, of course! As Barry tells her students:
Drawing is a language. It’s hard to understand what that really means until you’ve ‘spoken’ and ‘listened’ to it enough in a reliable regular way like the reliable regular way we will have together this semester.
That’s an important definition for those lacking confidence in their drawing abilities to keep in mind. Barry may revere the inky blacks of comics legend Jaime Hernandez, but she’s also a devotee of the wild, unbridled line that may be a beginner’s truest expression. (Stick figures, however, “don’t cut it.”) To her way of thinking, everyone is capable of communicating fluently in visual language. The current crop of student work reveals a range of training and natural talent, but all are worthy when viewed through Barry’s lens.
The teacher’s philosophy is the binding element here, but don’t fret if you are unable to take the class in person:
We rarely speak directly about the work we do in our class though we look at it together. We stare at it and sometimes it makes us laugh or we silently point out some part of it to the classmate beside us. To be able to speak this unspoken language we need to practice seeing (hearing) the way it talks.
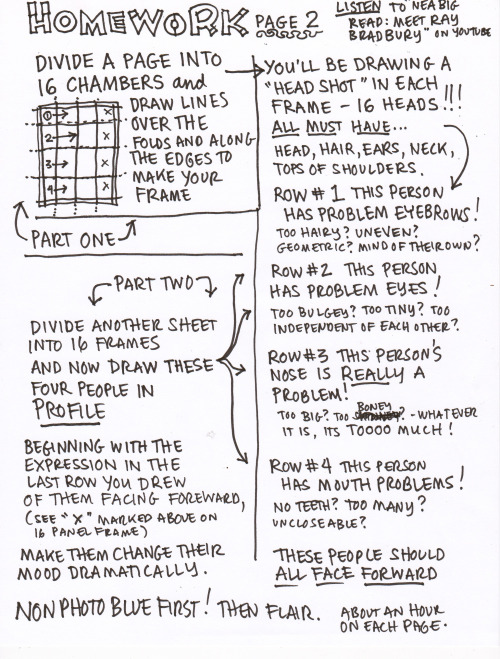
That earlier-alluded-to rigor is no joke. Daily diary comics, 3 minute self portraits on index cards, pages folded to yield 16 frames in need of filling, and found images copied while listening to prescribed music, lectures, and readings are a constant, non-negotiable expectation of all participants. Her methodology may sound goose‑y but it’s far from loose‑y.
In other words, if you want to play along, prepare to set aside a large chunk of time to complete her weekly assignments with the vigor demanded of non-virtual students.
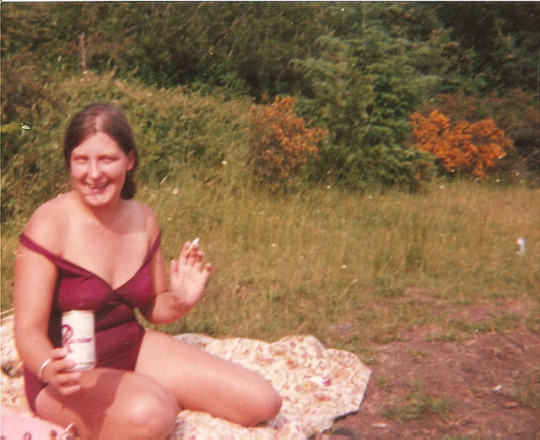

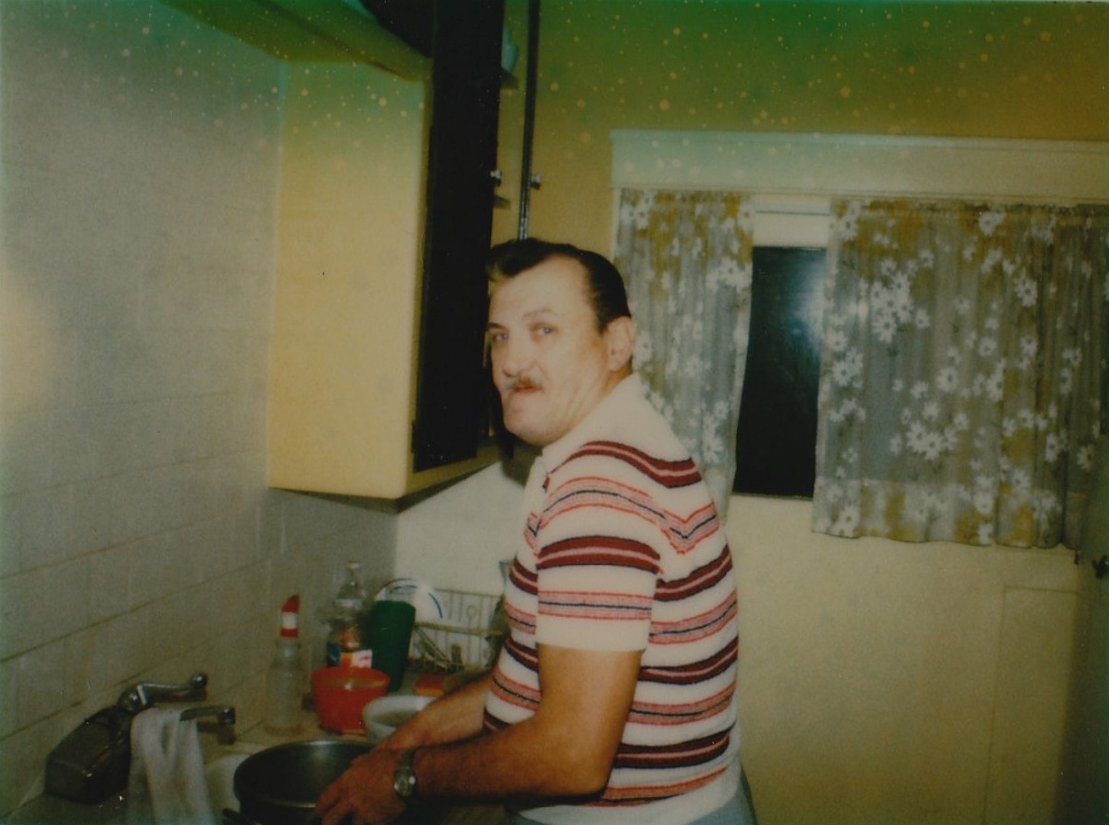
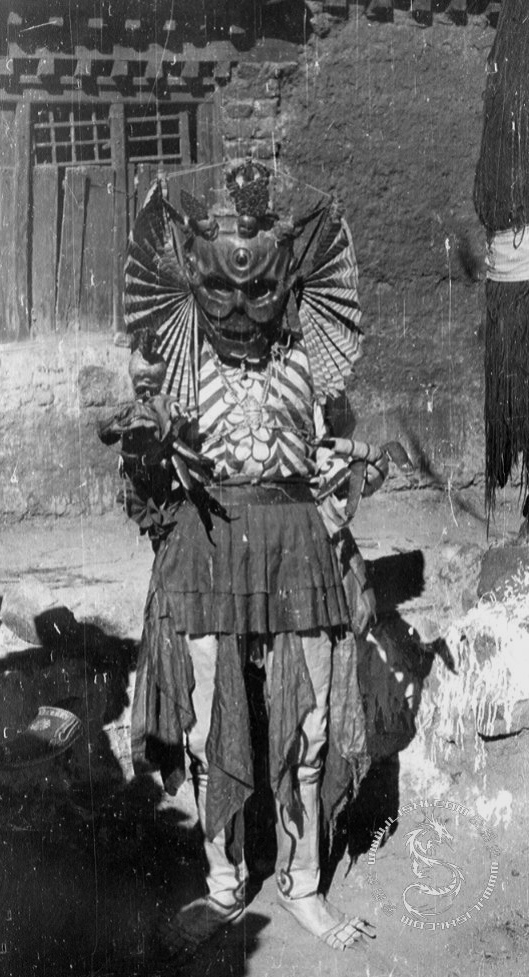
Those who aren’t able to commit to going the distance at this time can reconstruct the class later. Barry leaves both the assignments and examples of student work on her Tumblr for perpetuity. (You can see an example here.) For now, try completing the 20 minute exercise using the assigned image above, or by choosing from one of her “extra credit” images, below:
Set timer for three minutes and begin this drawing using a yellow color pencil. Try to draw as much of the drawing as you can in three minutes. You can draw fast, and in a messy way, The important thing is to get as much covered as you can in three minutes. You can color things in if you like. Look for the darkest areas of the photo and color those in.
Set a timer for another three minutes and using your non-dominant hand, draw with orange or color pencil to draw the entire drawing again, drawing right on top of the first drawing layer. The lines don’t have to match or be right on top of each other, you can change your mind as you add this layer. You can move a bit to the right rather than try to draw directly onto the first set of lines.
Set a timer for another 3 minutes and use a red pencil and draw it again, using you dominant hand, adding another layer to the drawing. Again, you don’t have to follow your original lines. Just draw on top of them.
Set a timer for another 3 minutes and use a dark green pencil to draw the entire drawing one more time on top of all the others.
Set a timer for 8 minutes and use a dark blue pencil to draw it one more time.
Spend the last 8 minutes inking the image in with your uniball pen. Remember that solid black is the very last thing you’d do given your time limit. You want to make sure to draw all the parts of the picture first.






Related Content:
Cartoonist Lynda Barry Shows You How to Draw Batman in Her UW-Madison Course, “Making Comics”
Watch Lynda Barry’s Graduation Speech; Give a Shout Out to the Teachers Who Changed Your Life
1,700 Free Online Courses from Top Universities
Ayun Halliday is an author, illustrator, and Chief Primatologist of the East Village Inky zine. Follow her @AyunHalliday