From the paranoid fundamentalist tracts of Jack Chick, to Ronald McDonald promoting scouting, to an upcoming graphic novel explaining the science of climate change, comics and graphic novels have long been a means of both proselytizing and informing, condensing complex narratives into a digestible format with broad appeal. The medium is so elastic, it can seemingly adapt itself to any kind of story, even the most soberly serious and historically significant. For example, Georgia Congressman John Lewis, veteran of the Civil Rights movement, chose to tell his story—in collaboration with co-writer Andrew Aydin and artist Nate Powell—as a graphic novel called March (making him the first lawmaker to appear at a Comic-Con). Part one of three was published late last year and rose to the top of the New York Times and Washington Post bestseller lists. March has also become an important resource for teachers and librarians (download a free 11-page teachers guide from publisher Top Shelf here).
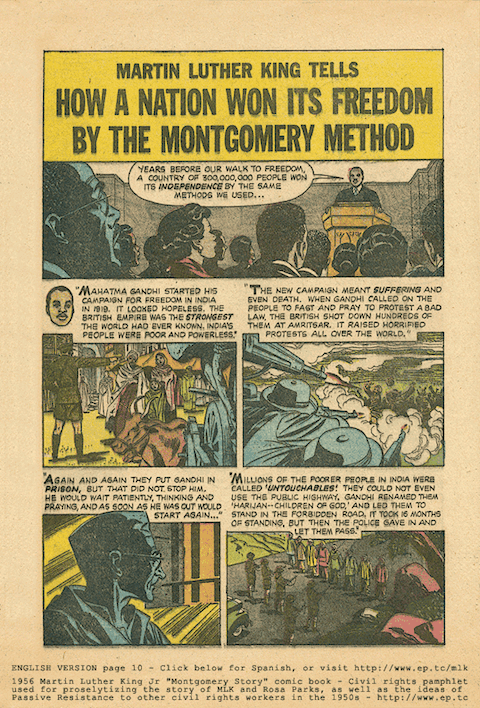
Lewis’ choice of medium may seem motivated by the current esteem in which the form is held in scholarly and popular circles alike, but he was primarily influenced by a much earlier civil rights comic book, Martin Luther King and the Montgomery Story. (See cover up top. Read it online here.) Begun just five months after Rosa Parks’ historic refusal, the comic aimed to disseminate the epic tale of the Montgomery, AL bus boycott throughout the South. A section called “The Montgomery Method” (first page above) instructs readers on the nonviolent resistance techniques employed by civil rights workers in Alabama, with a primer on Gandhi and his influence on King. In the short video below, see NYU professor and King scholar Sylvia Rhor explain the genesis of the comic in the work of Alfred Hassler, then leader of Civil Rights organization Fellowship of Reconciliation. Hassler, a little-known figure who died in 1991, is now receiving more recognition through similar means. He himself recently became the subject of a graphic novel project (and now documentary) called The Secret of the 5 Powers about his work with Buddhist peace activists Thich Nhat Hanh and Sister Chan Khong during the Vietnam War.
As Rhor notes above, the King comic has had tremendous influence, not only in the past, and not only on Rep. Lewis in the present. In 2003–2004, The Montgomery Story was translated into Arabic, and Egyptian revolutionaries during the Arab Spring found inspiration in the comic book that “turned Martin Luther King into a superhero”
Related Content:
200,000 Martin Luther King Papers Go Online
MLK’s Last Days and Final Speech
Josh Jones is a writer and musician based in Durham, NC. Follow him at @jdmagness