“I first took on The Lord of the Rings at the age of eleven or twelve,” writes The New Yorker’s Anthony Lane. “It was, and remains, not a book that you happen to read, like any other, but a book that happens to you: a chunk bitten out of your life.” The preteen years may remain the most opportune ones in which to pick up the work of J.R.R. Tolkien, but whatever the period in life at which they find their way in, most readers who make the journey through Middle-earth never really leave the place. And it hardly requires covering much more ground to get from hungering to know everything about the world of The Lord of the Rings — one rich with its own terrain, its own races, its own languages — to hungering to know how Tolkien created it.

Now the countless Lord of the Rings enthusiasts in America have their chance to behold the materials first-hand. The exhibition Tolkien: Maker of Middle-Earth, which runs from January 25th to May 12th of this year at New York’s Morgan Library and Museum, will assemble “the most extensive public display of original Tolkien material for several generations,” drawing from “the collections of the Tolkien Archive at the Bodleian Library (Oxford), Marquette University Libraries (Milwaukee), the Morgan, and private lenders.”
All told, it will include “family photographs and memorabilia, Tolkien’s original illustrations, maps, draft manuscripts, and designs related to The Hobbit, The Lord of the Rings, and The Silmarillion.”
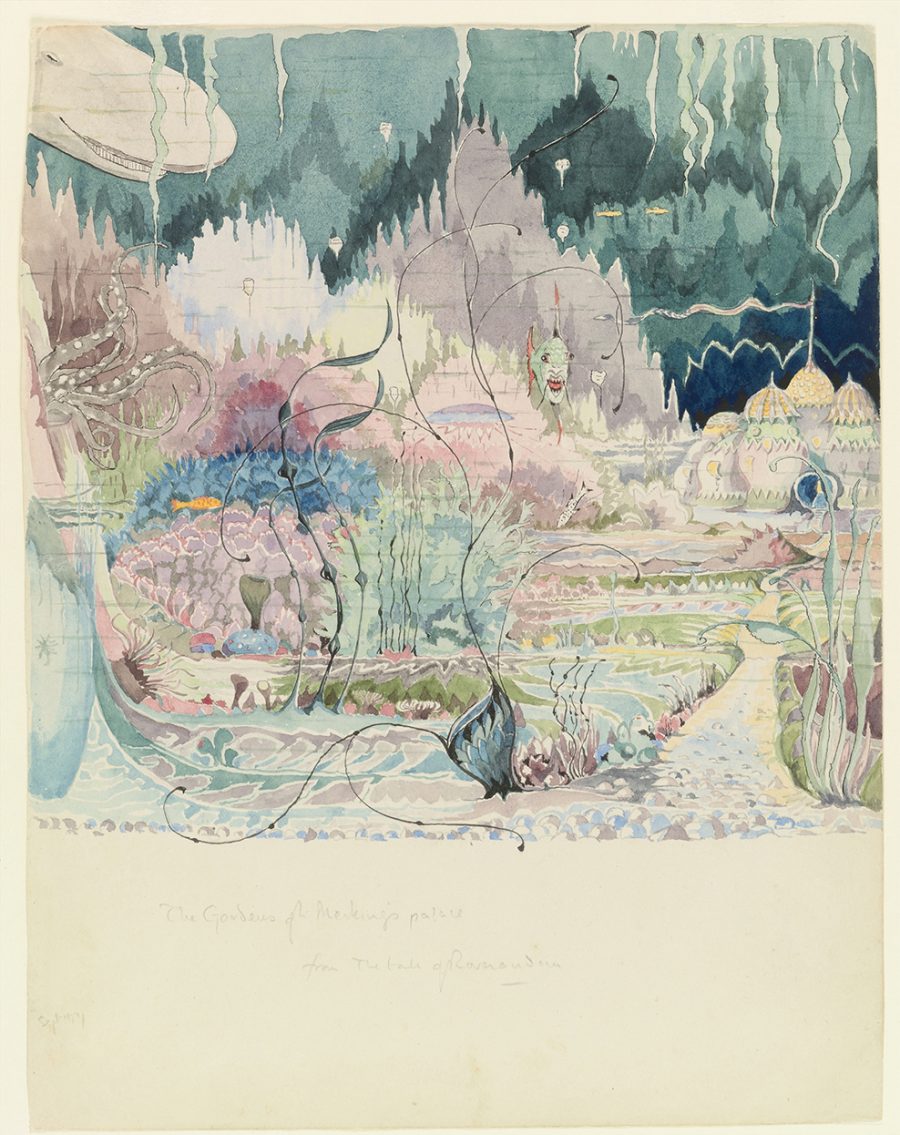

Mental Floss’ Emily Petsko also highlights the presence of “original illustrations of Smaug the dragon (from The Hobbit), Sauron’s Dark Tower of Barad-dûr (described in The Lord of the Rings and The Silmarillion), and other recognizable characters,” as well as that of Tolkien’s draft manuscripts that “provide a window into his creative process, as well as the vivid, expansive worlds he created.” You can see more of the things Tolkienian that will soon come available for public viewing at the Morgan in the exhibition’s trailer at the top of the post.
“The Lord of the Rings has remained comically divisive,” Lane writes. “It is either adored, with varying degrees of guilt, or robustly despised, often by those who have yet to open it.” But after seeing an exhibition like Tolkien: Maker of Middle-Earth, even Tolkien’s harshest critics may well find themselves persuaded to acknowledge the scale and depth of the books’ achievement, as well as the dedication and even bravery of its creator. As Lane puts it, “The Lord of the Rings may be the final stab at epic, and there is invariably something risky, if not downright risible, in a last gasp.” But “Tolkien believed that he could reproduce the epic form under modern conditions,” the fruit of that belief continues to enrapture readers of all ages more than 60 years later.
If you can’t wait for the exhibition, you might want to have a look at Wayne G. Hammond and Christina Scull’s book, J.R.R. Tolkien: Artist and Illustrator. It’s already published.

via AM New York and Mental Floss
Related Content:
110 Drawings and Paintings by J.R.R. Tolkien: Of Middle-Earth and Beyond
Discover J.R.R. Tolkien’s Personal Book Cover Designs for The Lord of the Rings Trilogy
Hear J.R.R. Tolkien Read From The Lord of the Rings and The Hobbit
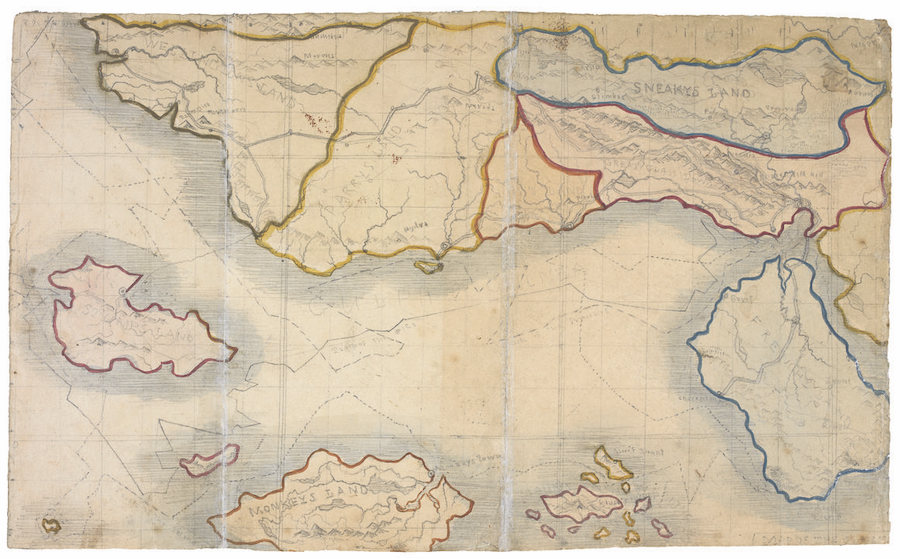
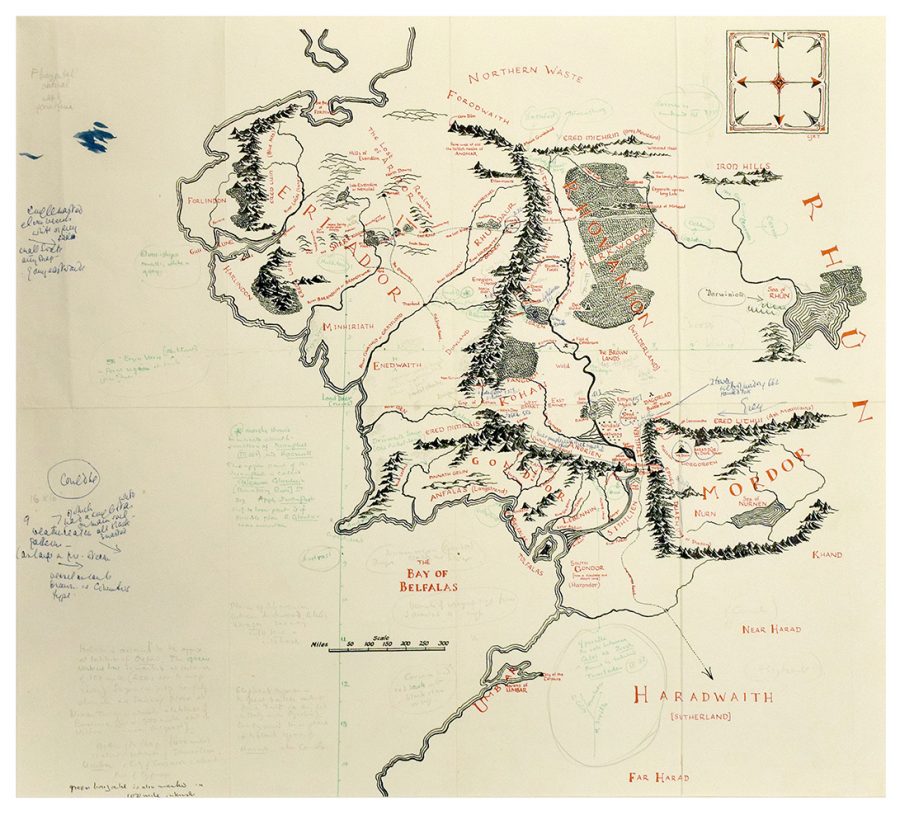
Map of Middle-Earth Annotated by Tolkien Found in a Copy of Lord of the Rings
Based in Seoul, Colin Marshall writes and broadcasts on cities, language, and culture. His projects include the book The Stateless City: a Walk through 21st-Century Los Angeles and the video series The City in Cinema. Follow him on Twitter at @colinmarshall or on Facebook.