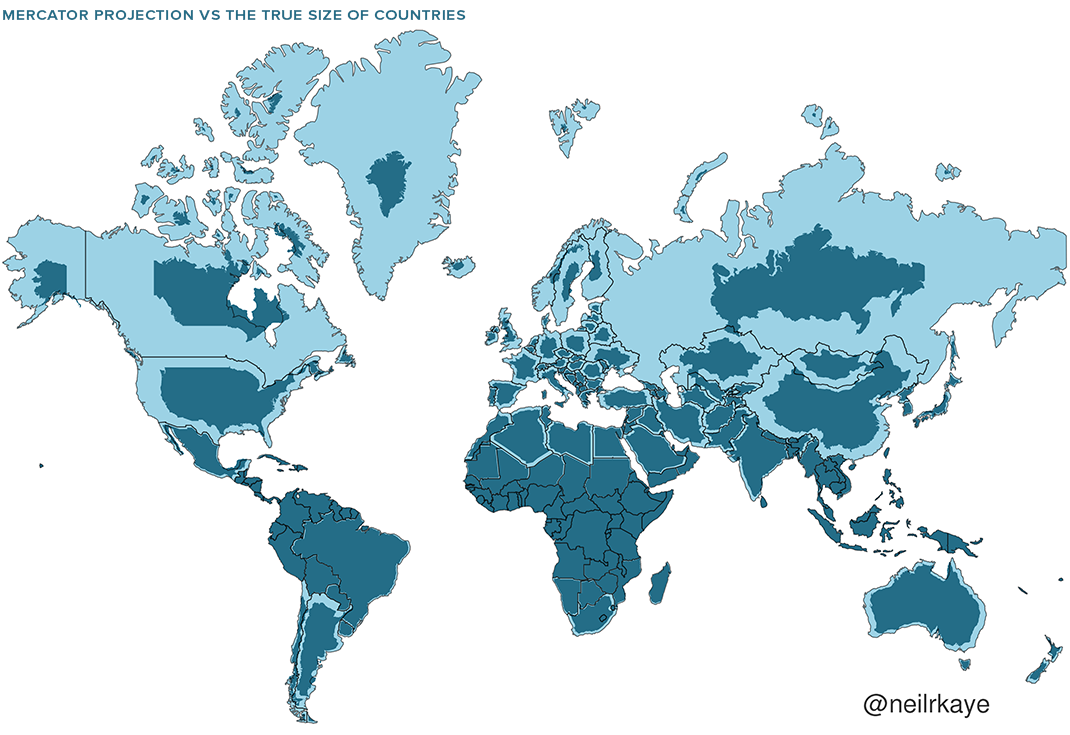
Younger fans might find it hard to believe, but David Bowie was not exactly at the height of coolness when he first appeared in David Lynch’s Twin Peaks: Fire Walk with Me in 1992. The overblown Glass Spider tour was five years earlier, followed by a Greatest Hits tour in 1990. He had tried to reinvent himself with Tin Machine for two albums. In fact, with Ryko rereleasing his catalog on CD, it looked mostly like Bowie would spend the rest of his career cashing in on nostalgia.
The same criticisms were hurled at Lynch after the Cannes premiere of the Twin Peaks “prequel”. Quentin Tarantino, who was at that Cannes premiere and heard the collective boos from the audience, said “David Lynch had disappeared so far up his own ass that I have no desire to see another David Lynch movie until I hear something different.”
But whaddya know? It turns out that the rest of the ‘90s were very good for both artists. Lynch went on to make some of his best work, and Fire Walk With Me is now considered a classic. Bowie wound up working with Eno again on the uncompromising and dense Outside.
Now Bowie has only one scene in Fire Walk With Me, but goddamn if it isn’t one of the best in the movie. I distinctly remember the chill that shot up my spine just before Bowie’s Philip Jeffries–an FBI field agent who escapes the Black Lodge–makes his crazed appearance in Philadelphia. Like a quantum particle, he is both there and not there, walking through a freeze frame of Agent Cooper as the FBI’s security cameras lock up.
“I’m not going to talk about Judy,” he says. “In fact we’re not gonna talk about Judy at all.”
The “Missing Pieces” version on the FWWM DVD shows the entire scene as it plays out as shot, with Jeffries breaking down in pain before being teleported back to a hotel in Buenos Aires. It’s pretty straightforward and a bit clunky.
In the official FWWM cut, Lynch and his editor Mary Sweeney work some special Black Lodge alchemy.
“Who do you think that is there?” Jeffries says, pointing at Coop as blue static fades in over the scene. Two realities then vie for power: Jeffries’ gnomic warnings versus his visions from a visit to the Black Lodge, the space above the convenience store, where all sorts of spirits live, lurk, and wait. Angelo Badalamenti’s score groans and shrieks and runs backwards. The scene is dense with clues and menace, and once things in the FBI office return to “normal,” Jeffries is gone.
“We live inside a dream,” Jeffries had warned, and 25 years later in Twin Peaks: The Return, Cooper himself would deliver a similar line inside another police station, as two realities played over each other, double-exposed.
David Bowie wouldn’t return to Lynch-world as an actor, but the director used his Outside song, “I’m Deranged,” as the opening and closing music to 1997’s Lost Highway, a track like that FWWM scene teeters on the brink of madness, filled with cut-and-paste lyrics and Mike Garson’s insane piano runs.
When Lynch announced the return of Twin Peaks, and after the passing of Bowie, fans wondered if by some miracle Jeffries would appear on the screen. Had Lynch managed to grab footage of the singer, like he had done for Catherine Coulson, so close to their exit?
Instead, when Evil Cooper finally met Jeffries again, it was as a machine–fans jokingly called it a gigantic tea kettle–that both spoke in English and puffed out numbers/clues in a cloud of steam.
Bowie reportedly never liked his 1992 performance because of his Louisiana accent, so when Lynch informed Bowie through his lawyer about his character’s return, Bowie asked for it to be redubbed by a real actor from Louisiana: Nathan Frizzell. (It may be authentic, but it ain’t no Bowie.)
Related Content:
Dave: The Best Tribute to David Bowie That You’re Going to See
Watch All of the Commercials That David Lynch Has Directed: A Big 30-Minute Compilation
Watch an Epic, 4‑Hour Video Essay on the Making & Mythology of David Lynch’s Twin Peaks
Ted Mills is a freelance writer on the arts who currently hosts the artist interview-based FunkZone Podcast and is the producer of KCRW’s Curious Coast. You can also follow him on Twitter at @tedmills, read his other arts writing at tedmills.com and/or watch his films here.