It’s been over a month since public health precautions led almost every school in the United States to switch to online instruction.
While there are obviously much greater tragedies unfolding daily, it’s hard not to empathize with students who have watched countless special events—proms, commencements, spring sports, performances, hotly anticipated rites of passage—go poof.
In New York City, students in Parsons School of Design’s Narrative Spaces: Design Tools for Spatial Storytelling course were crestfallen to learn that their upcoming open-to-the-public exhibition of group and solo projects in the West Village—the centerpiece of the class and a huge opportunity to connect with an audience outside of the classroom—was suddenly off the menu.
Multidisciplinary artist Jeff Stark, who co-teaches the class with Pamela Parker, was disappointed on their behalves.
Stark’s own work, from Empire Drive In to Miss Rockaway Armada, is rooted in live experience, and New York City holds a special place in his heart. (He also edits the weekly email list Nonsense NYC, an invaluable resource for independent art and Do-It-Yourself events in the city.)
This year’s class projects stemmed from visits to the City Reliquary, a small museum and civic organization celebrating everyday New York City artifacts. Students were able to get up close and personal with Chris Engel’s collection of photographs, menus, promotional materials, and souvenirs documenting the heyday of New York’s supper club nightlife, from the 1940s through the 1960s.
Student Rylie Cooke, an Australian who aspires to launch a design company, found that her research deepened her connection to artifacts she encountered at the Reliquary, as she came to appreciate the fabled Copacabana’s influence on the popular culture, food, and music of the period:
… with COVID-19 it became important to have this connection to the artifacts as I wasn’t able to physically touch or look at them when Parsons moved to online for the semester. I am a very hands-on creative and I love curating things, especially in an exhibit format.
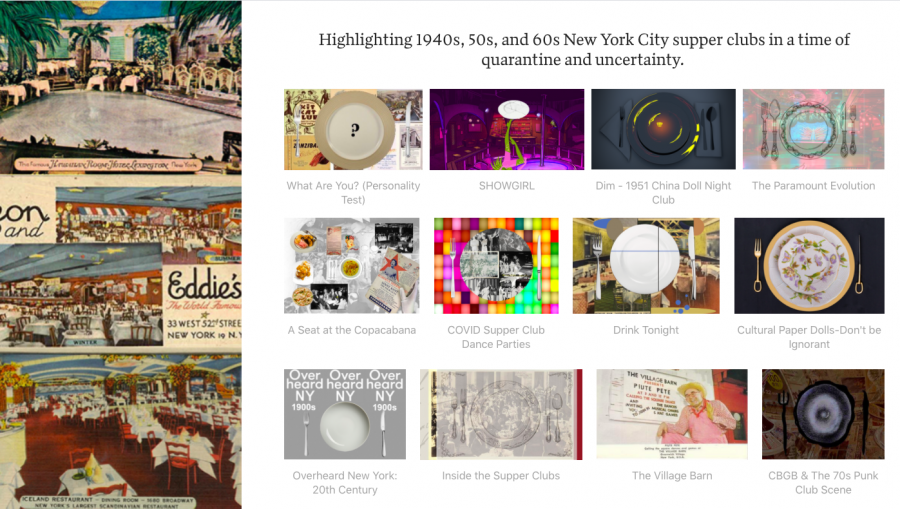
Rather than scrap their goal of public exhibition, the class decided to take things into the virtual realm, hustling to adapt their original concepts to a purely screen-based experience, The New York Supper Club: From Nightlife to Social Distancing.
The plan to wow visitors with a period-appropriate table in the center of their West Village exhibition space became a grid of digital placemats that serve as portals to each project.

Cooke’s contribution, A Seat at the Copacabana, begins with an interview in which baseball great Mickey Mantle recounts getting into a cloakroom brawl as he and fellow New York Yankees celebrated a birthday with a Sammy Davis Jr. set. Recipes for steak and potatoes, Chicken a la King, rarebit, and arroz con pollo provide flavor for a floorshow represented by archival footage of “Let’s Do the Copacabana” starring Carmen Miranda, a Martin and Lewis appearance, and a dance rehearsal from 1945. The tour ends at the Copa’s current incarnation in Times Square, with a vision of pre-socially distanced contemporary merrymakers salsa-ing the night away.
(Navigate this exhibit using toolbar arrows at the bottom of the screen.)
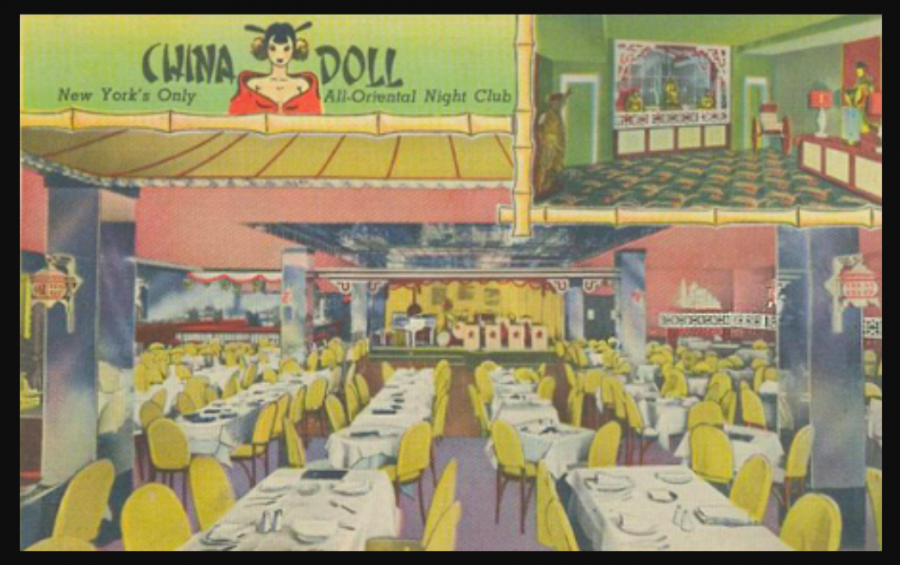

Student Hongxi Chen’s investigations into The China Doll nightclub resulted in an elaborate interactive immersive experience on the topic of cultural appropriation:
The China Doll… was founded in 1946 by Caucasian stage producer Tom Ball, who deemed it the only “all-oriental” night club in New York. While the club sometimes played off “Oriental” stereotypes, and titled one of its shows “Slant-Eyed Scandals,” they featured Asian dancers and Asian singers presenting popular songs in a way New Yorkers had never seen before. The Dim interactive experience unfolds with the story of Thomas, a waiter at the China Doll.
As a junior in Parsons’ Design and Technology program, Chen had plenty of previous experience forging virtual environments, but working with a museum collection was new to him, as was collaborating on a virtual platform.
He sought Stark’s advice on creating vivid dialogue for his fictional waiter.
Jiaqi Liuan, a Design and Technology MFA student and veteran of the Shanghai production of Sleep No More, Punchdrunk’s immersive retelling of MacBeth, helped choreograph Chen’s China Doll dancers in an homage to The Flower Drum Song’s Fan Tan Fannie number.
Chen stayed up until 7 am for two weeks, devouring open source tutorials in an attempt to wrangle and debug the many elements of his ambitious project—audio, video, character models and animation, software, game engines, and game server platform.
As Chen noted at the exhibition’s recent Zoom opening (an event that was followed by a digital dance party), the massive game can be a bit slow to load. Don’t worry, it’s worth the wait, especially as you will have a hand in the story, steering it to one of five different endings.
Chen, an international student, could not safely return to China and has not left his student apartment since mid-March, but gamely states that remaining in the same time zone as his school allowed him to communicate efficiently with his professors and the majority of his classmates. (Cooke is back home in Australia.)
Adds Chen:
Even though we are facing a difficult circumstance under the pandemic and had to pivot our original ideas into a virtual presentation, I’m glad that our class was able to quickly change plans and adapt to the situation. This… actually inspired me a lot and opened up ways to invite and connect people with virtual artwork.

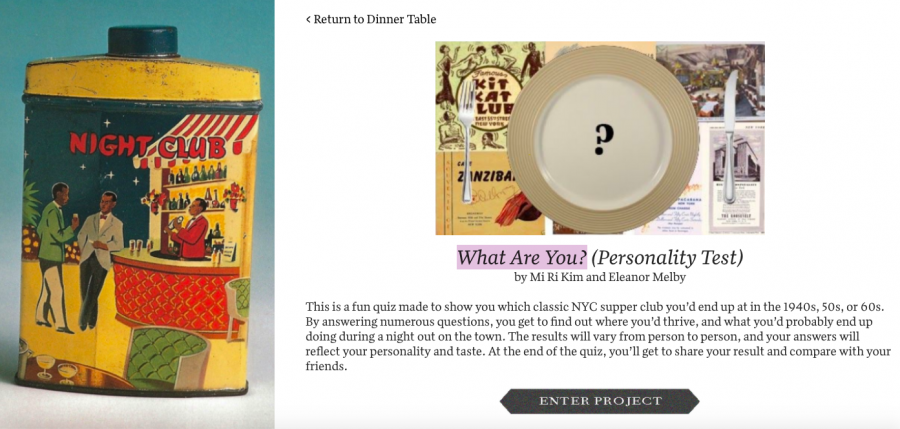
Other highlights of The New York Supper Club: From Nightlife to Social Distancing include Ming Hong Xian’s exploration of the famous West Village country music club, The Village Barn (complete with turtle races) and What Are You? a personality test devised by Mi Ri Kim and Eleanor Melby, to help visitors determine which classic NYC supper club best suits their personality.
(Apparently, I’m headed to Cafe Zanzibar, below, where the drinks are cheap, the aspirin is free, and Cab Calloway is a frequent headliner.)
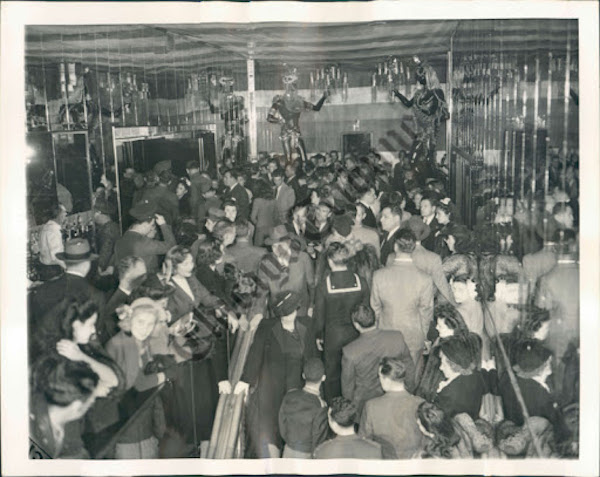

Stark admits that initially, his students may not have shared his swooning response to the source material, but they share his love of New York City and the desire to “get in the thick of it.” By bringing a Generation Z perspective to this historical ephemera, they stake a claim, making work that could help the City Reliquary connect to a new audience.
Enter The New York Supper Club: From Nightlife to Social Distancing here.
Explore the City Reliquary online here, and join in the civic pride by participating in its weekly Instagram Live events, including Thursday Collectors’ Nights.
(All images used with permission of the artists and The City Reliquary)
Related Content:
New York City: A Social History (A Free Online Course from N.Y.U.)
The Lost Neighborhood Buried Under New York City’s Central Park
Ayun Halliday is an author, illustrator, theater maker and Chief Primatologist of the East Village Inky zine. Her contribution to art in isolation is a hastily assembled tribute to the classic 60s social line dance, The Madison. Follow her @AyunHalliday.





