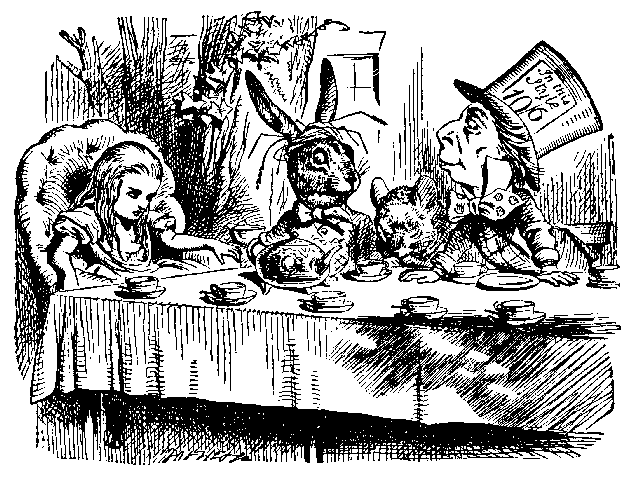
I never thought I could love an audio recording of Lewis Carroll’s Alice in Wonderland (technically Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland and its sequel, Through the Looking-Glass) more than I love the unabridged version narrated by Christopher Plummer. His wonderfully hammy characterizations and its six hour running time made it the perfect soundtrack for picking nits from the foot long tresses of a first-grader who’d been sent home with lice.
By the time she got the all clear, both of us had large portions of it committed to memory.
Christopher, I treasure the memories of those long hours spent together on cassette, but I’m afraid I’ll be spending the 150th anniversary of Alice with Sir John Gielgud, below.
Full leisurely we glide;
For both our oars, with little skill,
By little arms are plied,
While little hands make vain pretense
Our wanderings to guide.
He makes Lewis Carroll sound like Shakespeare!
The celebrated dry wit that served him so well throughout his illustrious career keeps this 1989 Alice very easy on the ears. He takes the opposite approach from Plummer, underplaying the character voices. It’s rare to find a gentleman of 85 who can play a 7‑year-old girl so convincingly, and with so little fuss.
In an extremely civilized bit of audio engineering, Gielgud recorded the tracks in the ballroom of Wyastone Leys, the Victorian country estate that is home to the audiobook’s label. Also? The English String Orchestra ushers listeners from scene to scene with excerpts from Mendelssohn’s String Symphonies. Ah…
Gielgud’s reading of Alice has been made available on Spotify. Find it here. Or embedded here. You can also find it on Youtube as well. Completists might also enjoy Gielgud’s turn as the Mock Turtle in Jonathan Miller’s superbly dark, black & white adaptation from 1966, here. (Gielgud makes his entrance at the 13:55 mark.)
To listen to Gielgud on Spotify, you will of course need Spotify’s software and account, both easy to come by: you just download and register.
Other readings of Alice can be found in our collection, 1,000 Free Audio Books: Download Great Books for Free.
Related Content
Free Audio: Alice In Wonderland Read by Cory Doctorow
Lewis Carroll’s Photographs of Alice Liddell, the Inspiration for Alice in Wonderland
Lewis Carroll’s Classic Story, Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland, Told in Sand Animation
Ayun Halliday will be appearing at the Brooklyn Book Festival in New York City next weekend.. Follow her @AyunHalliday