The snail may leave a trail of slime behind him, but a little slime will do a man no harm… whilst if you dance with dragons, you must expect to burn.
- George R. R. Martin, The Mystery Knight
As any Game of Thrones fan knows, being a knight has its downsides. It isn’t all power, glory, advantageous marriages and gifts ranging from castles to bags of gold.
Sometimes you have to fight a truly formidable opponent.
We’re not talking about bunnies here, though there’s plenty of documentation to suggest medieval rabbits were tough customers.
As Vox Almanac’s Phil Edwards explains, above, the many snails littering the margins of 13th-century manuscripts were also fearsome foes.
Boars, lions, and bears we can understand, but … snails? Why?
Theories abound.

Detail from Brunetto Latini’s Li Livres dou Tresor
Edwards favors the one in medievalist Lilian M. C. Randall’s 1962 essay “The Snail in Gothic Marginal Warfare.”
Randall, who found some 70 instances of man-on-snail combat in 29 manuscripts dating from the late 1200s to early 1300s, believed that the tiny mollusks were stand ins for the Germanic Lombards who invaded Italy in the 8th century.
After Charlemagne trounced the Lombards in 772, declaring himself King of Lombardy, the vanquished turned to usury and pawnbroking, earning the enmity of the rest of the populace, even those who required their services.
Their profession conferred power of a sort, the kind that tends to get one labelled cowardly, greedy, malicious … and easy to put down.
Which rather begs the question why the knights going toe-to- …uh, facing off against them in the margins of these illuminated manuscripts look so damn intimidated.
(Conversely why was Rex Harrison’s Dr. Dolittle so unafraid of the Giant Pink Sea Snail?)

Detail from from MS. Royal 10 IV E (aka the Smithfield Decretals)
Let us remember that the doodles in medieval marginalia are editorial cartoons wrapped in enigmas, much as today’s memes would seem, 800 years from now. Whatever point—or joke—the scribe was making, it’s been obscured by the mists of time.
And these things have a way of evolving. The snail vs. knight motif disappeared in the 14th-century, only to resurface toward the end of the 15th, when any existing significance would very likely have been tailored to fit the times.

Detail from The Macclesfield Psalter
Other theories that scholars, art historians, bloggers, and armchair medievalists have floated with regard to the symbolism of these rough and ready snails haunting the margins:
The Resurrection
The high clergy, shrinking from problems of the church
The slowness of time
The insulation of the ruling class
The aristocracy’s oppression of the poor
A critique of social climbers
Female sexuality (isn’t everything?)
Virtuous humility, as opposed to knightly pride
The snail’s reign of terror in the garden (not so symbolic, perhaps…)
A practical-minded Reddit commenter offers the following commentary:
I like to imagine a monk drawing out his fantastical daydreams, the snail being his nemesis, leaving unsightly trails across the page and him building up in his head this great victory wherein he vanquishes them forever, never again to be plagued by the beastly buggers while creating his masterpieces.
Readers, any other ideas?
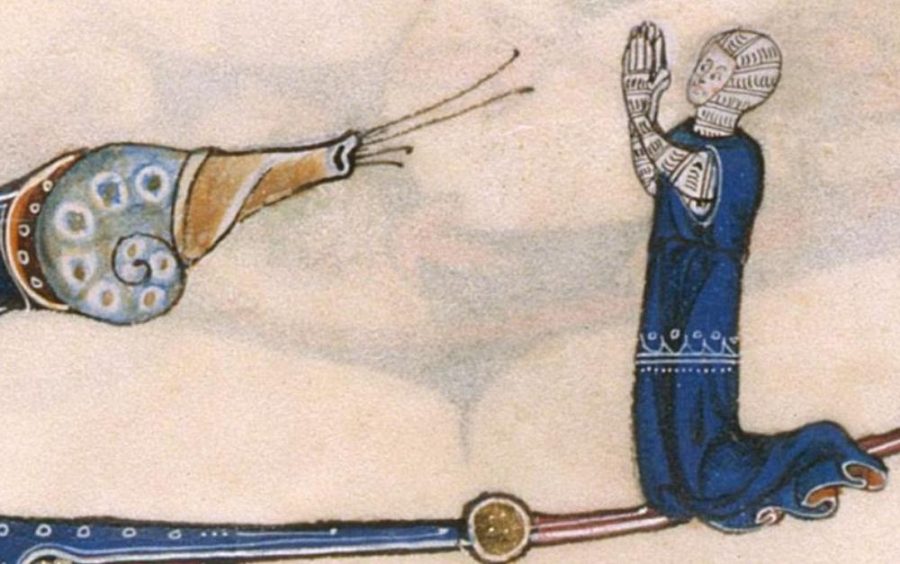
Detail from The Gorleston Psalter
Note: An earlier version of this post appeared on our site in 2019.
Related Content:
A Rabbit Rides a Chariot Pulled by Geese in an Ancient Roman Mosaic (2nd century AD)
Ayun Halliday is an author, illustrator, theater maker in New York City.