On a summer day in 1862, a tall, stammering Oxford University mathematician named Charles Lutwidge Dodgson took a boat trip up the River Thames, accompanied by a colleague and the three young daughters of university chancellor Henry Liddell. To stave off tedium during the five-mile journey, Dodgson regaled the group with a story of a bored girl named Alice who finds adventure in the most unexpected places. By the day’s end, Liddell’s middle daughter, also named Alice, was so enthralled by this account that she implored the mathematician to write the story down. Some three years later, Dodgson would publish Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland under the nom de plume of Lewis Carroll (the pen name is an Anglicized version of “Carolus Ludovicus,” the Latinized form of Charles Ludwidge). The perennial children’s read was immediately popular, counting Oscar Wilde and Queen Victoria among its ardent fans, and has never been out of print since its initial publication in 1865.

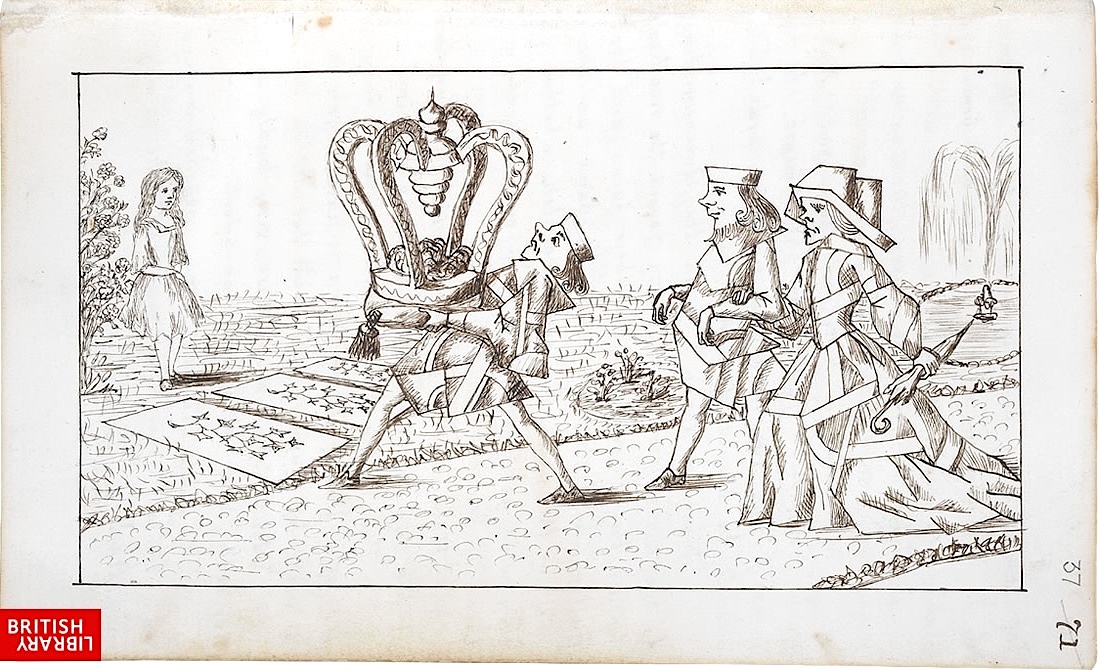
Alice’s Adventures Under Ground, the original version of the book that Carroll presented to Alice Liddell in 1864, is presently housed in the British Library, which has graciously made it freely available online. You can view it here. The handwritten volume includes 37 crisp ink illustrations, all personally drawn by Dodgson. Discerning Alice readers will notice that these illustrations differ from the iconic images (and, to my eyes, very much superior) created by famed Punch magazine political cartoonist John Tenniel.
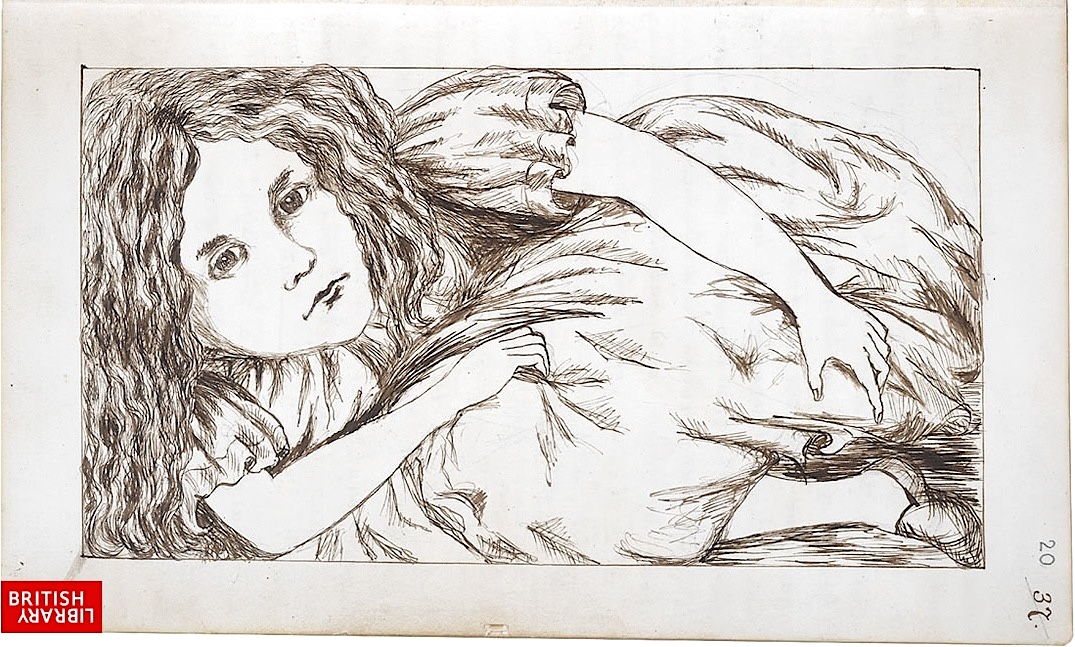

Title and illustrations aside, the original manuscript is considerably slimmer than the final version, containing roughly 12,000 fewer words.

Those wishing to revisit Alice’s adventures can do so at the Internet Archive.
Ilia Blinderman is a Montreal-based culture and science writer. Follow him at @iliablinderman.
Related Content:
See Salvador Dali’s Illustrations for the 1969 Edition of Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland
Meryl Streep Shrooms Her Way Through Modern Alice in Wonderland
The Real Alice in Wonderland Circa 1862, and Our Favorite Culture Links on the Web