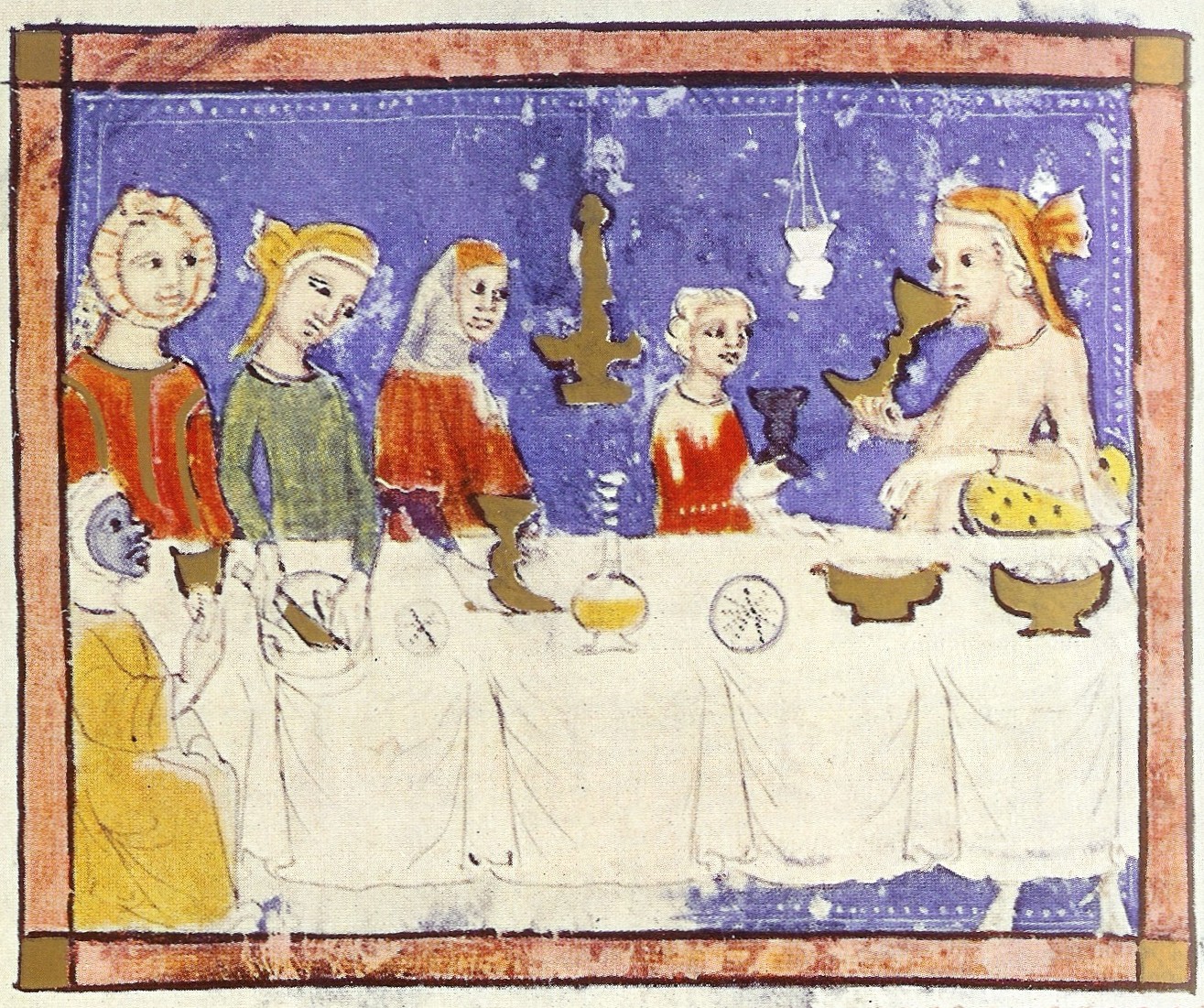
If you went to the doctor in late medieval Europe hoping to get a health complaint checked out, you could be sure of one thing: you’d have to hand over a urine sample. Though it dates back at least as far as the fourth millennium BC, the practice of uroscopy, as it’s called, seems to have been regarded as a near-universal diagnostic tool by the thirteenth century. At Medievalists.net, you can read excerpts of the then-definitive text On Urines, written about that time by French royal physician Gilles de Corbeil.
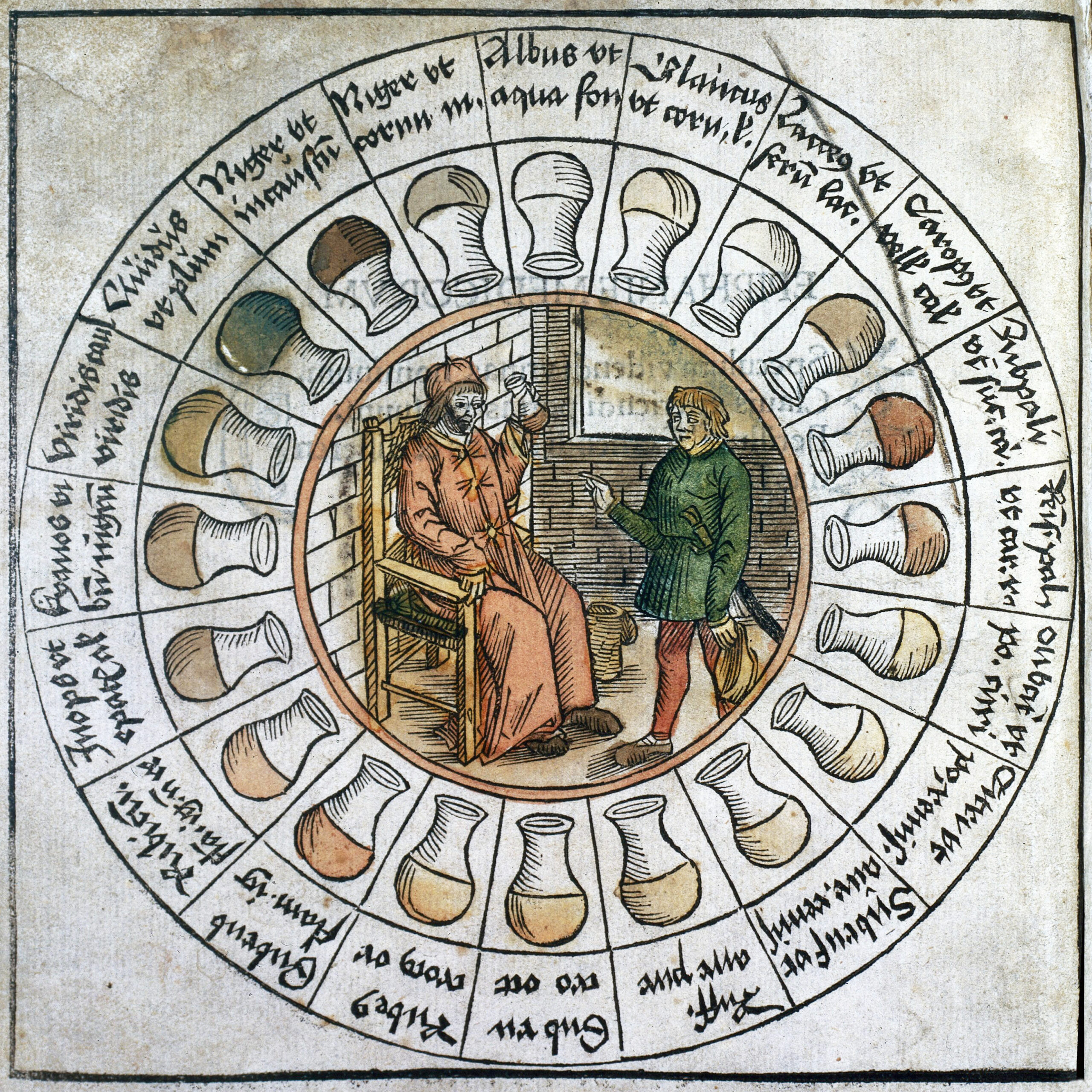
When a skilled physician examines a patient’s urine, de Corbeil explains, “health or illness, strength or debility, deficiency, excess, or balance, are determined with certainty.” Urine “darkened by a black cloudiness, and muddied with sediment, if produced on a critical day of an illness, and accompanied by poor hearing and insomnia, portends a flux of blood from the nose”; depending on other factors, “the patient will die or recover.”

Urine that looks livid near the surface could indicate a variety of conditions: “a mild form of hemitriteus fever; falling sickness; ascites; synochal fever; the rupture of a vein; catarrh, strangury; an ailment of the womb; a flux; a defect of the lungs; pain in the joints; consumptive phithisis; the extinction of natural heat.”
White urine could be a signal of everything from dropsy to lipothymia to hemorrhoids; wine-colored urine “means danger to health when it accompanies a continued fever; it is less to be feared if there is no fever.”
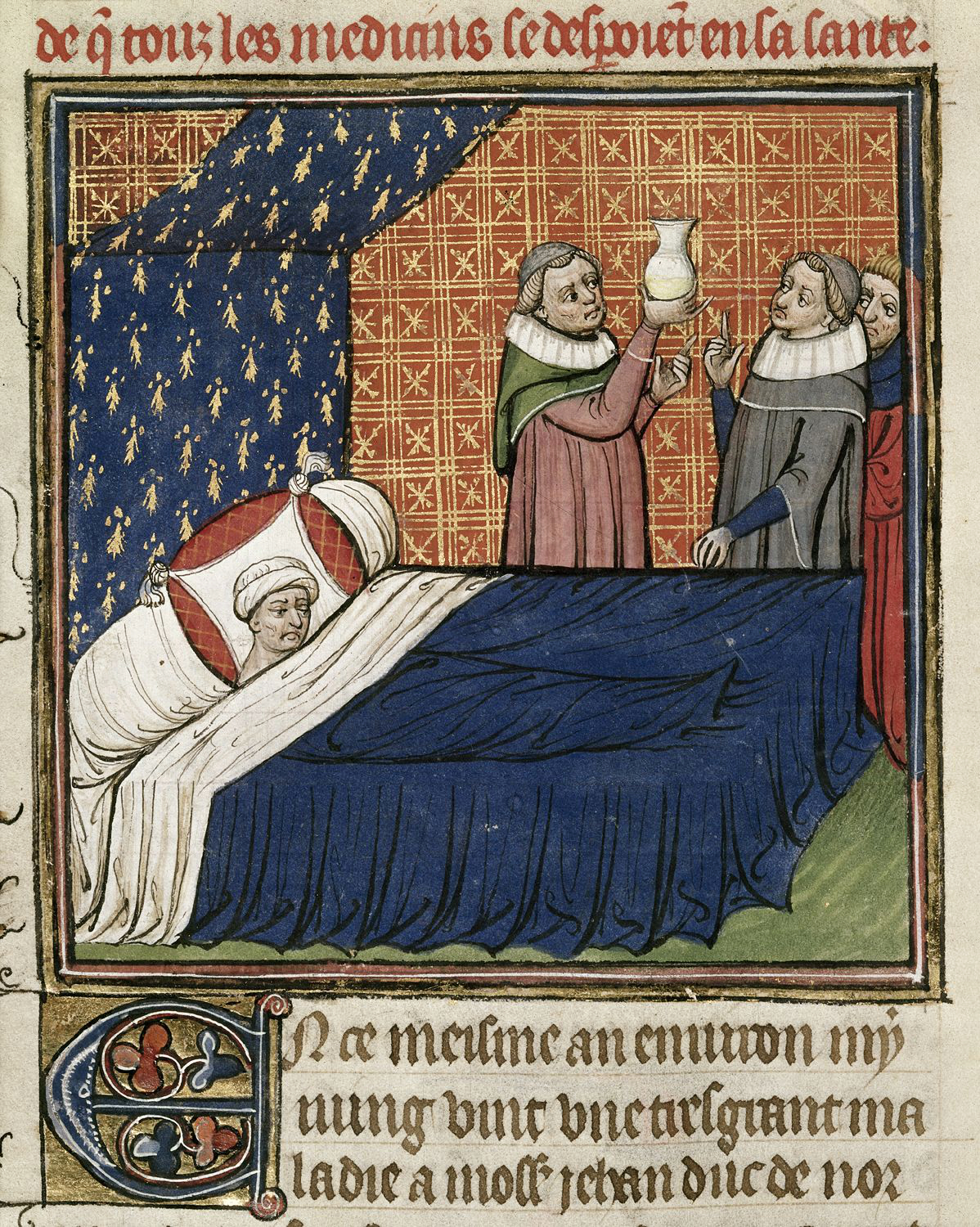
We may feel tempted, 800 years later, to discard all of this as pre-scientific nonsense. But compared with other diagnostic methods in the Middle Ages, uroscopy had a decent track record. “Urine was a particularly useful tool for diagnosing leprosy,” writes the Public Domain Review’s Katherine Harvey, “because the immediate physiological cause was thought to be a malfunctioning liver — an organ which was central to the digestive process, and thus any problems would be visible in the urine.” Indeed, “new forms of urine analysis have developed from these ancient traditions, and our present-day medical landscape is awash with urine samples.”
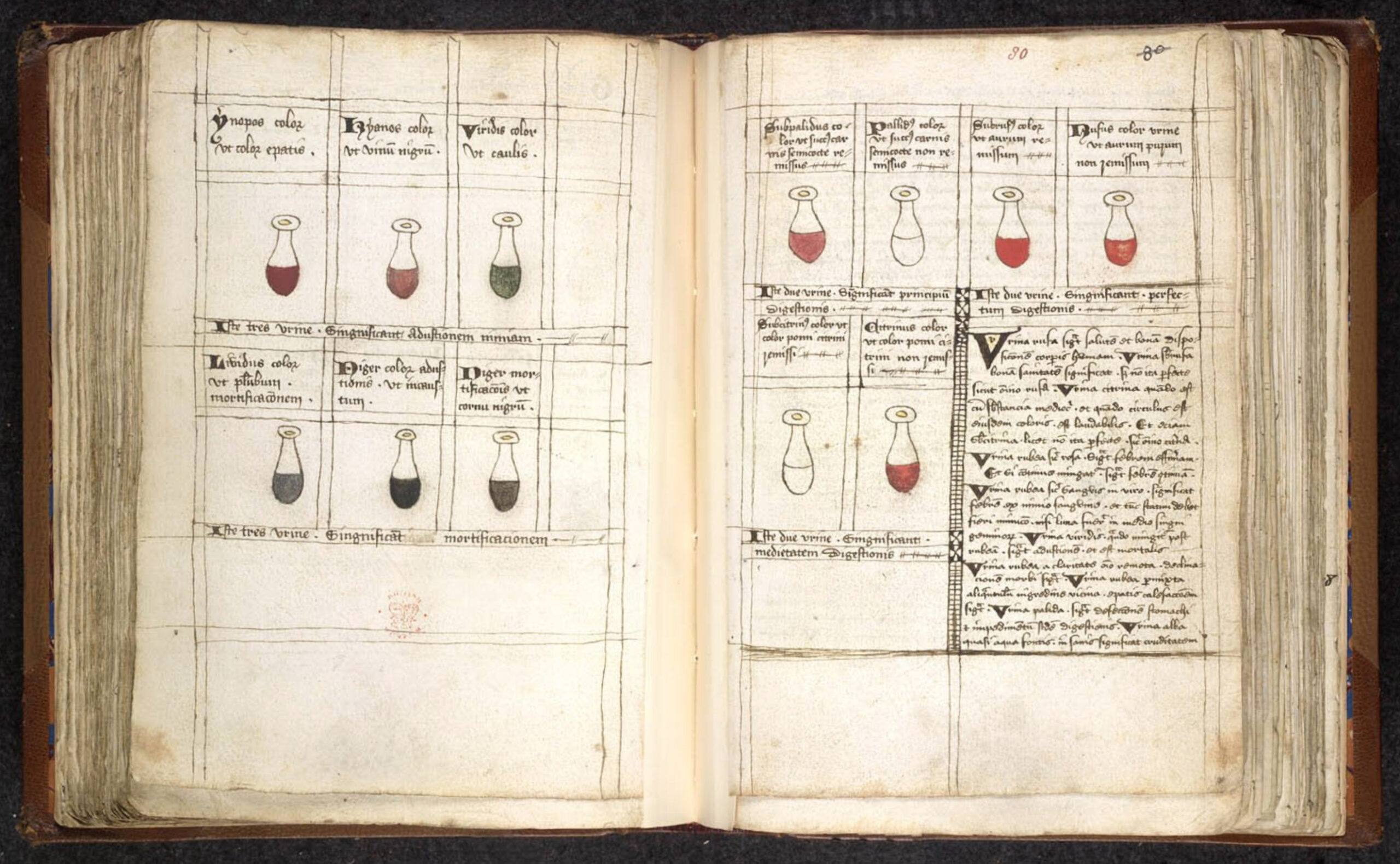
That’s certainly a vivid image, and so are the “urine wheels” that accompany Harvey’s piece: elaborate illustrations designed to help doctors identify the particular hue of a given sample, each one colored with the best pigmentation techniques of the time. But “there was no standardization,” notes Atlas Obscura’s Sarah Laskow, “and while some book publishers created detailed coloring instructions, the artisans who did the work didn’t always conform to those specifications.” As much prestige as these volumes surely exuded on the bookshelf, it was as true then as it is now that you become a good doctor not by reading manuals, but by getting your hands dirty.
Related content:
How the Brilliant Colors of Medieval Illuminated Manuscripts Were Made with Alchemy
1,000-Year-Old Illustrated Guide to the Medicinal Use of Plants Now Digitized & Put Online
Based in Seoul, Colin Marshall writes and broadcasts on cities, language, and culture. His projects include the Substack newsletter Books on Cities, the book The Stateless City: a Walk through 21st-Century Los Angeles and the video series The City in Cinema. Follow him on Twitter at @colinmarshall or on Facebook.















